Fig. 2. DUSP6 is modified by SUMO1 at K234.
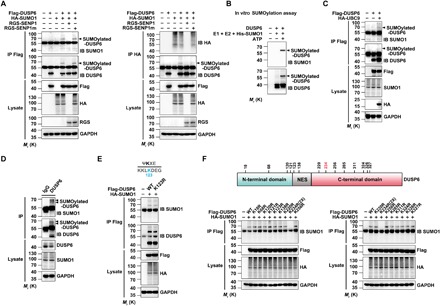
(A) DUSP6 is SUMO1-conjugated in vivo. Lysates from HeLa cells transiently transfected with empty vector (−), Flag-DUSP6, HA-SUMO1, RGS-SENP1, or RGS-SENP1m at various combinations as indicated for 24 hours were subjected to denaturing IP with anti-Flag (left) and anti-HA (right) antibodies, which was followed by IB using anti-SUMO1, anti-DUSP6, and anti-HA. The original lysates were also analyzed by IB with anti-Flag, anti-HA, anti-RGS for input, and anti–glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) for loading control. Arrowheads indicate SUMOylated DUSP6. (B) DUSP6 is SUMO1-conjugated in vitro. Purified recombinant DUSP6 was incubated with E1, E2, SUMO1, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in vitro at 37°C for 1 hour, and reaction was terminated with SDS loading buffer. The samples prepared above were analyzed by Western blotting with SUMO1 and DUSP6 antibodies as indicated. (C) DUSP6 conjugation by endogenous SUMO1 was enhanced by overexpression of UBC9. Lysates from HeLa cells transiently transfected with empty vector (−), Flag-DUSP6, or HA-UBC9 at various combinations as indicated for 24 hours were subjected to denaturing IP and IB as in (A) (left). (D) SUMO1 conjugation of endogenous DUSP6 in mouse brain. Lysates prepared from mouse cerebral cortices under denaturing conditions were subjected to IP with anti-DUSP6 antibody, followed by IB with anti-SUMO1 and anti-DUSP6 antibodies. The original lysates were also analyzed by IB using anti-DUSP6 and anti-SUMO1 for input and anti-GAPDH for loading control. Bands for SUMOylated-DUSP6 are indicated by arrowheads. (E) DUSP6 SUMOylation is not dependent on K123, the lysine residue that adheres consensus SUMO modification site (inset), as predicted for mouse DUSP6 using SUMOsp 2.0 software. Lysates from HeLa cells transiently cotransfected with HA-SUMO1 and Flag-DUSP6 or Flag-DUSP6K123R mutant, or vector control (−) as indicated for 24 hours, were subjected to IP with anti-Flag antibody, followed by IB with anti-SUMO1 and anti-DUSP6 antibodies. The original lysates were analyzed by IB using anti-Flag and anti-HA for input and anti-GAPDH for loading control. (F) Identification of K234 as the SUMO modification site of mouse DUSP6. Top: Diagram for domain organization of mouse DUSP6 and the locations of all lysine residues, except for K254, which is buried inside the protein and unlikely SUMOylatable based on the SUMOsp 2.0 software. NES, nuclear export signal. Bottom: Lysates from HeLa cells transiently cotransfected with HA-SUMO1, wild-type (WT) Flag-DUSP6, or one of the K➔R mutants of Flag-DUSP6, or the vector control (−) as indicated for 24 hours, were subjected to IP with anti-Flag antibody, followed by IB with anti-SUMO1. The original lysates were also analyzed by IB using anti-Flag and anti-HA for input and anti-GAPDH for loading control. Note that 2× amount of DUSP6K234R plasmid was used in the transfection to match the protein expression with the wild-type DUSP6 and other mutants. In (A) to (F), blots are representatives of at least three independent experiments.
