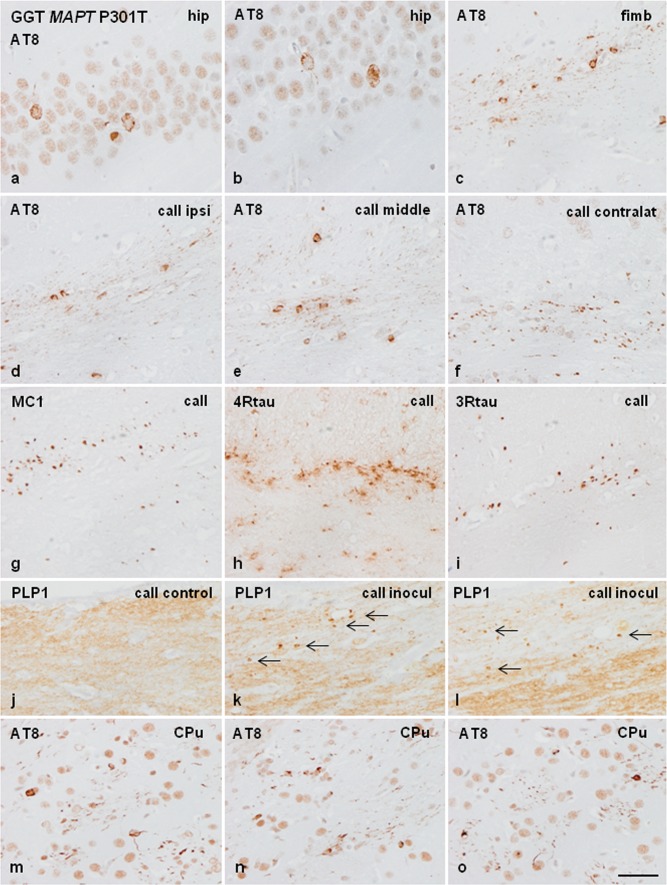
Fig. 10.
Phospho-tau deposits in neurons of the hippocampus (a, b) and in glial cells, threads, and dots in the fimbria (c) following unilateral inoculation of sarkosyl-insoluble fractions from the frontal cortex of GGT linked to MAPT P301T mutation into the right hippocampus of WT mice aged 12 months and killed 6 months later. Phospho-tau deposits are also seen in glial cells, threads, and dots in the ipsilateral (d), middle region (e), and contralateral corpus callosum (f) in mice inoculated at the age of 12 months and killed at the age of 18 months. Deposits are immunostained with antibodies MC-1 and anti-4Rtau (g, h). Some deposits are also identified with antibodies against 3Rtau (i). j–l PLP1 immunohistochemistry reveals reduced intensity and the presence of small PLP1-immunoreactive dots (arrows) in the corpus callosum in mice after 4 and 7 months following unilateral inoculation of sarkosyl-insoluble fractions from GGT linked to MAPT P301T mutation when compared with controls. m–o Phospho-tau deposits in the CPu following unilateral inoculation in the right caudate/putamen in mice aged 10 months and killed 5 months later; deposits are found in neurons, glial cells, and numerous threads in the stripes. hip hippocampus, fimb fimbria, callipsi middle, contralat corpus callosum ipsilateral, middle region and contralateral, call corpus callosum, CPu caudate/putamen. Paraffin sections processed for immunohistochemistry slightly counterstained with haematoxylin, bar = 50 μm