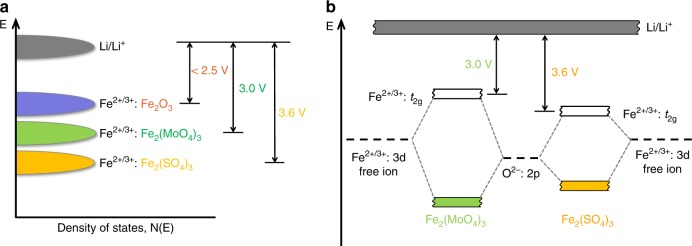
Fig. 4. Role of counter-cations in shifting the redox energies in polyanion oxides.
a Lowering of the redox energies of the Fe2+/3+ couple and the consequent increase in cell voltage on going from a simple oxide Fe2O3 to a polyanion oxide Fe2(MoO4)3 and then to another polyanion oxide Fe2(SO4)3 with a more electronegative counter-cation S6+ vs. Mo6+, i.e., with a more covalent S–O bond than the Mo–O bond. b Molecular orbital energy diagram illustrating the lowering of the Fe2+/3+ redox energy in Fe2(SO4)3 compared to that in the isostructural Fe2(MoO4)3, due to a weakening of the Fe–O covalence by a more covalent S–O bond than the Mo–O bond through inductive effect.