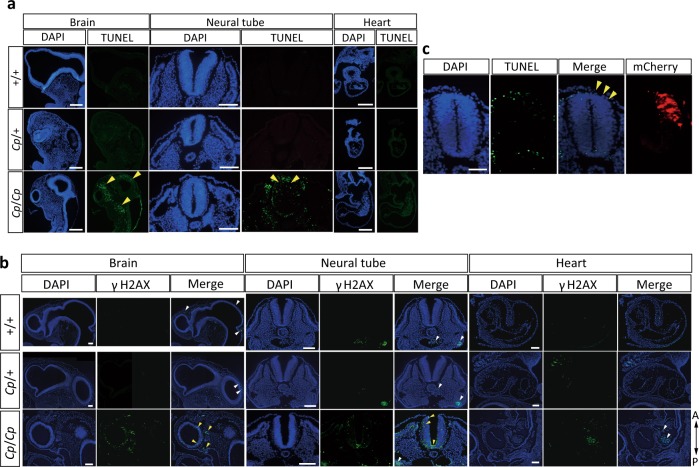
Fig. 5. Detection of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in the E3 embryos from the GSP/Cp strain.
a Detection of DSBs by TUNEL staining in the brain, neural tube, and heart. The sections are oriented with the rostral side up and the caudal side down for the brain, and the dorsal side up and the ventral side down for the neural tube. A sagittal section of the ventricle is shown for the heart. Nuclear localization was visualized with DAPI. The yellow arrowheads indicate DSBs detected by TUNEL staining. Bar, 100 μm. b The detection of DSBs by immunofluorescence staining with an anti-γH2AX antibody in the brain, neural tube, and heart. γH2AX signaling in the mesenchymal cells of the brain and neural tube in the Cp/Cp embryos are indicated with yellow arrowheads. The white arrowheads indicate non-specific fluorescence signals in the blood cells. Bar, 100 μm. c Exogenous NHEJ1 expression was introduced on the right side of the neural tube by electroporation in the E2 Cp/Cp embryos, and DSBs were detected by TUNEL staining. The images are oriented with the dorsal side up and the ventral side down. Nuclear localization is visualized with DAPI, and the electroporated area is visualized with mCherry fluorescence. The yellow arrowheads indicate the regions where DSBs are rescued by exogenous NHEJ1 expression. Bar, 50 μm.