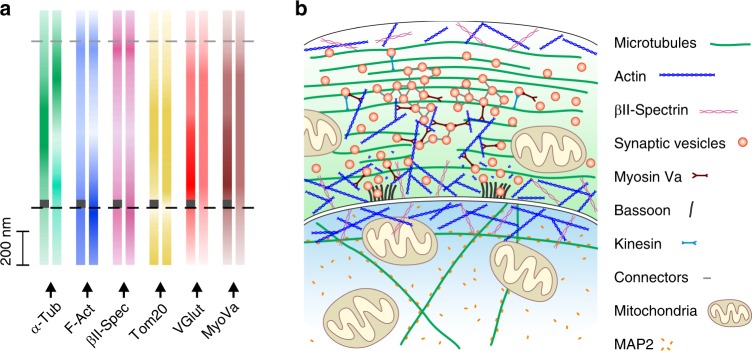
Fig. 4. Model of protein distribution in the calyx of Held synapse.
a Distribution of proteins examined in Fig. 3 and Supplementary Fig. 13 indicated by color gradient. Distribution at active zone (AZ)-positive regions are indicated by dark gray rectangles at the bottom of color gradient bars. b Model of synaptic architecture at the calyx of Held. Predominantly peripheral distribution of F-actin paralleled by βII-spectrin distribution. Note the decreased presence of polymerized actin in AZ regions. Microtubules are distributed throughout the presynapse with AZ-containing regions more densely populated by tubulins. Synaptic vesicles (SVs) cover up the whole presynaptic space. At the presynaptic membrane, SVs are more abundant in AZ-proximal regions. The distribution of myosin Va (MyoVa) is highly correlated with the vesicular VGlut1 signal underpinning its role in SV trafficking: MyoVa is known to mediate the vesicular transfer from microtubules along which they are transported by kinesin motors to actin filaments. Interestingly, together with actin, MyoVa might be involved in SV clustering, similarly to connectors (structures of unknown molecular identity interconnecting SVs). In addition to the membrane-binding WGA lectin, the anatomy of the calyx synapse was traced using bassoon as the AZ marker. The mitochondrial protein Tom20 is present in pre- and postsynaptic compartments, whereas MAP2 is specifically expressed at the postsynapse.