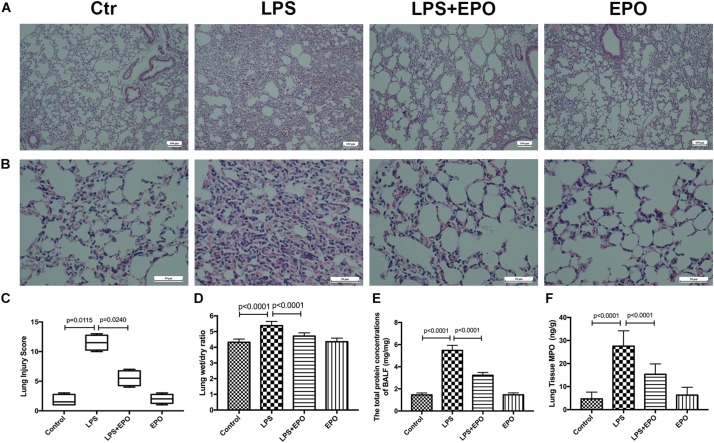
FIGURE 1.
EPO mitigated LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. EPO (5 U/g) was injected into the peritoneal cavity of mice after LPS (15 mg/kg) stimulation. The mice were sacrificed 8 h later, and the effects of EPO were assessed in (A,B) hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections (original magnification × 100, × 400). Lung injury scores (C) were recorded from 0 (no damage) to 16 (maximum damage) according to the criteria described in Section “Materials and Methods.” The lung wet/dry ratio (D) was tested to evaluate pulmonary edema. The total protein concentrations in the BALF (E) were measured to reflect the integrity of the pulmonary alveolar-capillary barrier. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) concentrations in lung tissues (F) were measured by ELISA to quantitatively determine the resolution of infiltrated cells. The lung injury score data are presented as medians and ranges (5th –95th percentile), and the differences among groups were assessed by Kruskal–Wallis test and the post hoc test (Dunn’s method) was applied to investigate the differences one by one. n = 4 per group. The other data are presented as the mean ± SD. The differences of D–F were assessed by one-way ANOVA and the post hoc test (Turkey method) was applied to investigate the differences one by one. n = 8 per group.