Figure 5. A20 as a dual enzyme in NF-κB signalling.
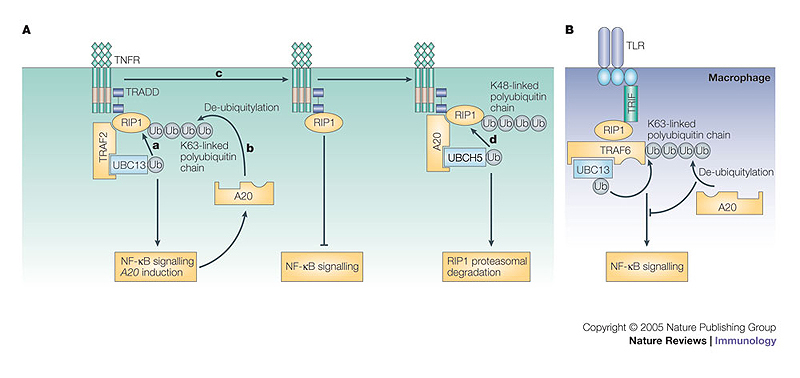
A | Stimulation through tumour-necrosis factor (TNF) receptors (TNFRs) causes TNFR-associated factor 2 (TRAF2)-mediated K63 (Lys63)-linked polyubiquitylation of receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1) (a), which results in the downstream activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). A20 then functions first as a de-ubiquitylating enzyme to remove K63-linked polyubiquitin chains (b), which terminates TNF-mediated signalling (c). At this stage, A20 then functions as an E3 ligase through recruitment of the ubiquitin-bound E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme H5 (UBCH5), facilitating the transfer of ubiquitin from UBCH5 to RIP1 and promoting K48-linked polyubiquitylation of RIP1 (d) and subsequent degradation of RIP1. B | A20 also functions as a de-ubiquitylating enzyme to remove K63-linked polyubiquitin chains from TRAF6, a mediator of Toll-like receptor (TLR) signalling. TRADD, TNFR-associated via death domain; TRIF, Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR)-domain-containing adaptor protein inducing interferon-β.
