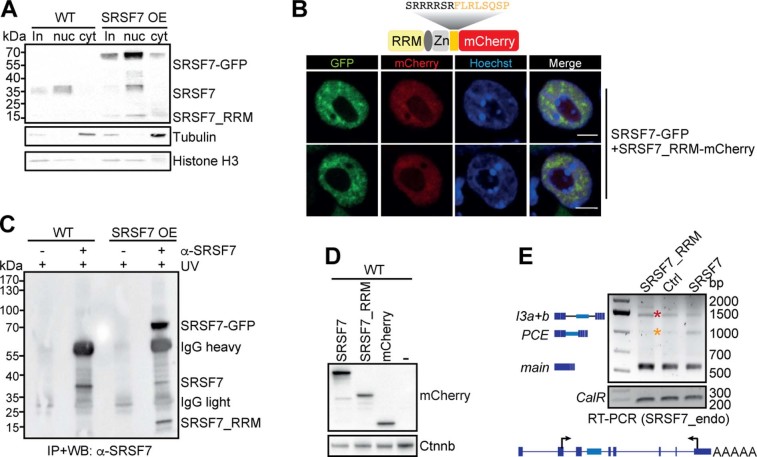
Extended Data Fig. 3. SRSF7_RRM competes with SRSF7 for binding to SRSF7-PCE transcripts and inhibits splicing of intron 3.
a, WB analysis of cytoplasmic (cyt) and nuclear (nuc) fractions of WT and SRSF7 OE cells. The blot was probed with α-SRSF7 as well as with α-Histone H3 and α-Tubulin antibodies to verify the fractionation efficiency. b, Confocal microscopy following transient expression of SRSF7_RRM-mCherry in SRSF7-GFP expressing cells. DNA was stained with Hoechst. c, WB analysis of iCLIP samples to validate the IP efficiency. Samples without antibodies served as controls. Blots were probed with α-SRSF7. d, WB showing the comparable expression of full-length SRSF7-mCherry, SRSF7_RRM-mCherry and empty mCherry plasmids in P19 WT cells. Blots were probed with α-mCherry and α-Beta-Catenin (Ctnnb) as loading control. e, RT-PCR of SRSF7 isoforms generated from the endogenous SRSF7 gene in WT cells transfected with plasmids transiently overexpressing full-length SRSF7-mCherry, SRSF7_RRM-mCherry or empty mCherry using the indicated primers.