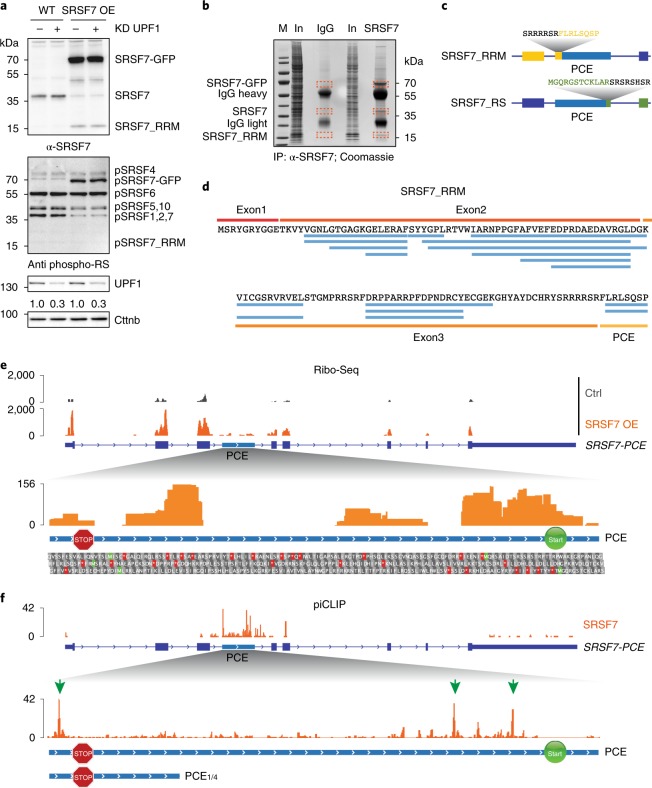
Fig. 2. The SRSF7-PCE isoform is translated into two distinct truncated SRSF7 proteins.
a, WB analysis of WT and SRSF7 OE cells upon knockdown (KD) of UPF1. The membrane was probed with antibodies to α-SRSF7, mAb104 (antiphospho-RS) and α-UPF1. The KD efficiency is indicated below the UPF1 blot. β-catenin (Cttnb) was used as loading control. b, Coomassie-stained SDS–PAGE gel of stringent IP to purify the SRSF7_RRM isoform for MS analysis. Cut bands are indicated in orange boxes. IgG, unspecific antibody control; M, marker; In, input. c, Scheme of two truncated SRSF7 proteins encoded by the SRSF7-PCE transcript. Sequences of the unique C- and N-termini are shown above in yellow and green, respectively. d, Identified peptides (FDR < 0.05) mapping to exons 1–3 and the PCE. e, Top: distribution of Ribo-Seq reads from WT (Ctrl) and SRSF7 OE samples on the SRSF7 gene. The PCE is indicated in light blue. Bottom: distribution of Ribo-Seq reads within the PCE. Start (AUG, green Ms) and stop codons (red asterisks) as well as amino acids encoded in all three possible open reading frames are shown below. A STOP sign marks the termination codon of SRSF7_RRM. A START sign marks the putative initiation codon of SRSF7_RS. f, Top: distribution of SRSF7 piCLIP X-links on the SRSF7 gene. Bottom: distribution of SRSF7 piCLIP X-links in the PCE and PCE1/4 regions. The main binding peaks are highlighted with green arrows. Uncropped images for a are available as source data.