Figure 4. Histopathology of the asthmatic airway.
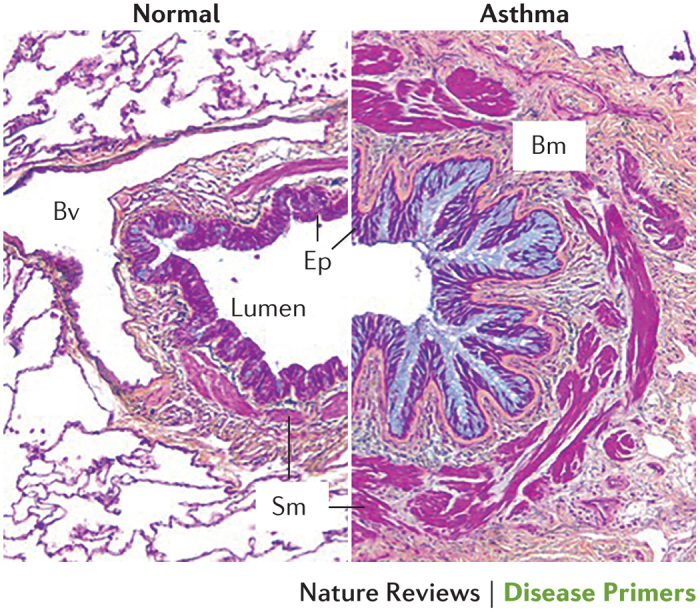
Cross section of a severe asthmatic airway (right) compared with a normal airway (left). Asthma involves mucosal inflammation that most frequently consists of activated eosinophils, mast cells and T lymphocytes within the context of a remodelled airway with mucous metaplasia, an increase in smooth muscle (Sm), fibrosis and angiogenesis. Bm, basement membrane; Bv, blood vessel; Ep, epithelium. Republished with permission of Dove Medical Press, from Clinical update on the use of biomarkers of airway inflammation in the management of asthma. Wadsworth, S., Sin, D. & Dorscheid, D., 4, 2011; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
