Figure 2. Signalling by BDCA2, DCIR and MICL antagonizes TLR signalling.
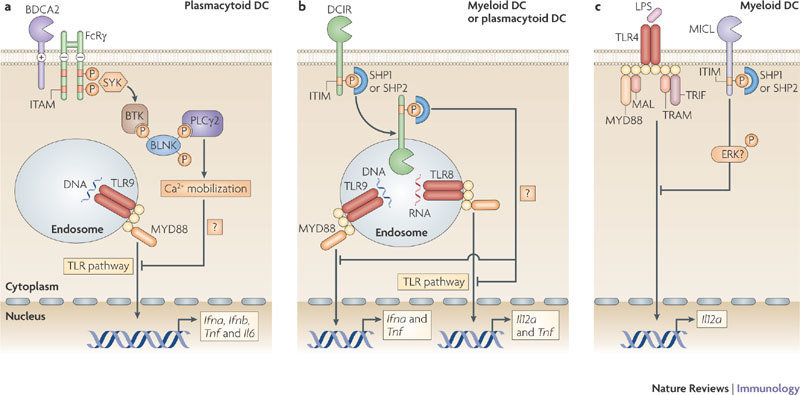
a | Activation of blood DC antigen 2 protein (BDCA2) leads to the recruitment of spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) to the phosphorylated immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of the paired signalling adaptor Fc receptor γ-chain (FcRγ). SYK activation leads to the activation of a complex consisting of B cell linker (BLNK), Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) and phospholipase Cγ2 (PLCγ2), which induces Ca2+ mobilization. The signalling pathway downstream of this complex is not fully known, but results in the downregulation of Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9)-induced production of interferon-α (IFNα), IFNβ, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) by plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs). Calcium mobilization might be involved in inhibiting the recruitment of myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MYD88) and thereby reducing the production of TLR-induced cytokines. b | Activation of DC immunoreceptor (DCIR) leads to its internalization into endosomal compartments, where TLR8 and TLR9 reside. The phosphorylation of its immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) recruits the phosphatases SH2-domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 (SHP1) or SHP2, which induces the activation of an unidentified signalling pathway that leads to the downregulation of TLR8-induced IL-12 and TNF production or TLR9-induced IFNα and TNF production by either myeloid or plasmacytoid DCs, respectively. c | Cross-linking of myeloid C-type lectin-like receptor (MICL) on myeloid DCs also results in the phosphorylation of its ITIM and the recruitment of SHP1 or SHP2. MICL activation has been shown to induce the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). However, it is not known whether ERK activation is involved in the downregulation of TLR4-induced IL-12 production. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MAL, MYD88-adaptor-like protein; TRAM, TRIF-related adaptor molecule; TRIF, TIR-domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFNβ.
