Figure 4. PA-IL and PA-IIL inhibitors.
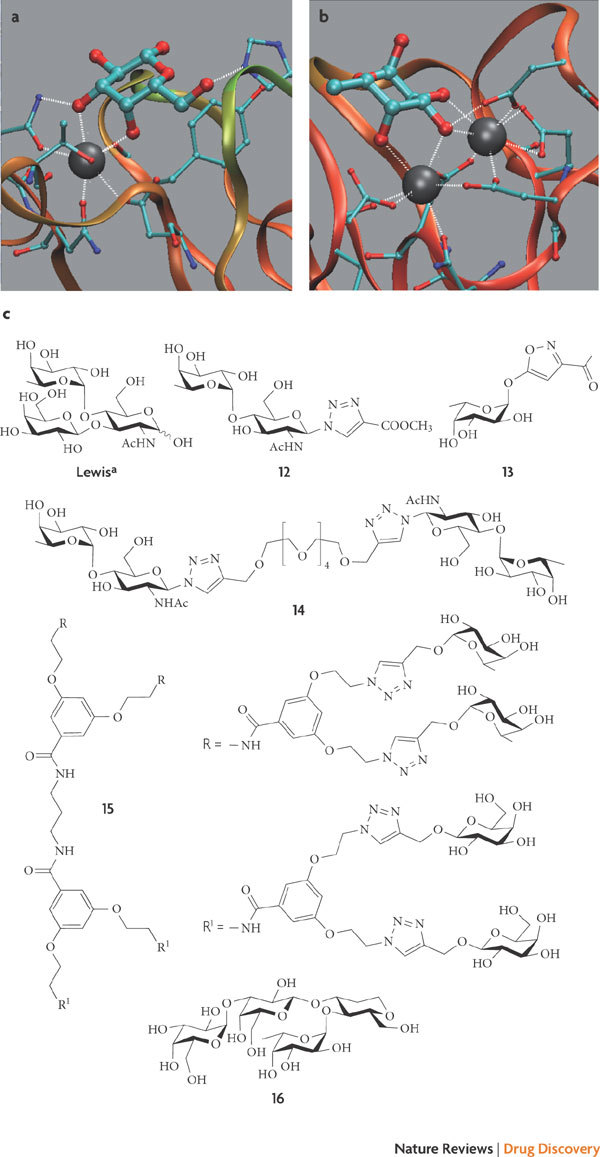
a | Binding sites of PA-I galactophilic lectin (PA-IL) complexed with D-galactose (Protein Data Bank code: 1OKO (Ref. 170)). b | Binding sites of fucose-binding lectin PA-IIL complexed with L-fucose (PDB code: 1GZT143). In parts a and b, the protein backbones are depicted in ribbon style, carbohydrates are shown in ball and stick style and the grey spheres are Ca2+. c | The monovalent ligands compound 12 (Ref. 101) and compound 13 (Ref. 99) exhibit affinity for PA-IL and PA-IIL that is similar to that of Lewisa (Ref. 100); the most potent oligovalent ligand is compound 14 (Ref. 102), but it has only a modest effect on a per saccharide basis; the heterobifunctional glycodendrimer compound 15 (Ref. 104) and the low-molecular-mass glycomimetic compound 16 (Ref. 105) bind to both PA-IL and PA-IIL from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
