Figure 1. The 'window period' in microbiological screening of potential organ donors.
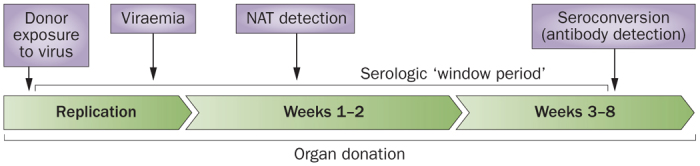
The development of an antibody response against a pathogen requires weeks to months after the initial infectious exposure. The time between the infectious exposure and the development of antibodies that can be detected by microbiological assays is called the window period. Serologic testing during this period might result in false-negative results. NAT measures viral nucleic acids, often using signal amplification techniques. Depending on the performance characteristics of the assay and the amount of virus present in the clinical specimen, NAT tends to detect infection earlier and with greater sensitivity than the corresponding serologic test. However, false-positive assays are generally more common with NAT testing. Abbreviation: NAT, nucleic acid test.
