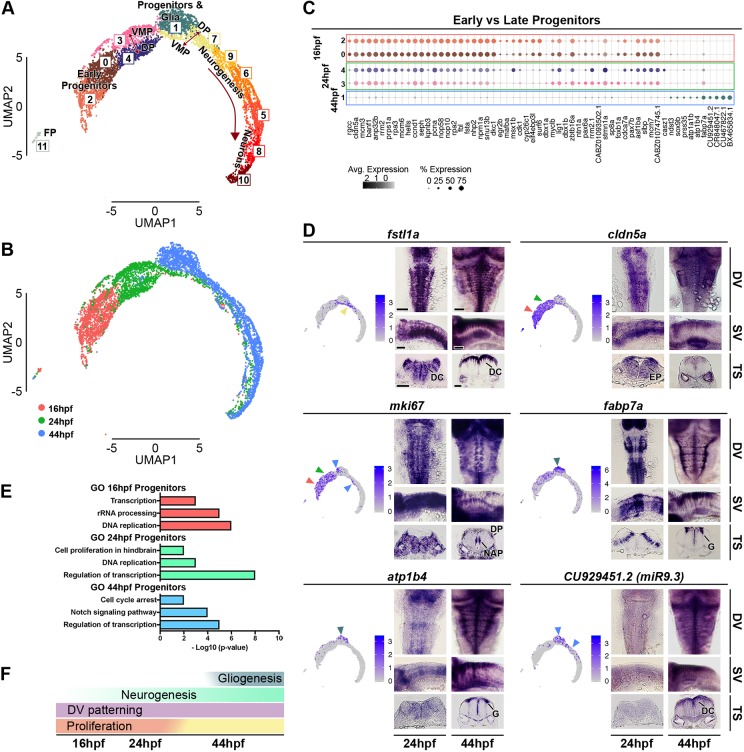
Fig. 5.
Analysis of aggregated 16 hpf, 24 hpf and 44 hpf data. (A) Unsupervised UMAP plot of cells from 16 hpf, 24 hpf and 44 hpf subdivides them into 12 clusters (DP, dorsal progenitors; VMP, ventral-medial progenitors; FP, floor plate). (B) UMAP plots with cells coloured based on their stage of origin: 16 hpf (pink), 24 hpf (green) and 44 hpf (blue). (C) Dot plot showing molecular signature of dorsal and ventral progenitors at the three stages. Dot size corresponds to the percentage of cells expressing the feature in each cluster, while the colour represents the average expression level. The full gene list of top 30 significantly enriched factors is in Fig. S8. (D) UMAP plots showing the log normalised counts of representative genes. Colour intensity is proportional to the expression level of a given gene. Whole-mount in situ hybridisation showing the expression pattern of cldn5a, fstl1a, mki67, fabp7a, atp1b4 and CU929451.2 (miR9.3) at 24 hpf and 44 hpf. Arrowheads indicate relevant domains of expression; colour refers to the cluster of origin. Dorsal view (DV), side view (SV) and 40 µm hindbrain transverse section (TS) at the level of r4-r5/r5-r6 are shown for each gene. Scale bars: 50 µm. EN, early neurogenesis; EP, early progenitors; DC, differentiating cells; DP, dorsal progenitors; NAP, non-apical proliferation; G, glia. (E) Selected Gene Ontology (GO) terms at 16 hpf (pink), 24 hpf (green) and 44 hpf (blue) are shown. x-axis is -log10 (P-value). (F) Summary of global hindbrain changes along the temporal axis.