Figure 1. Human antibody techniques.
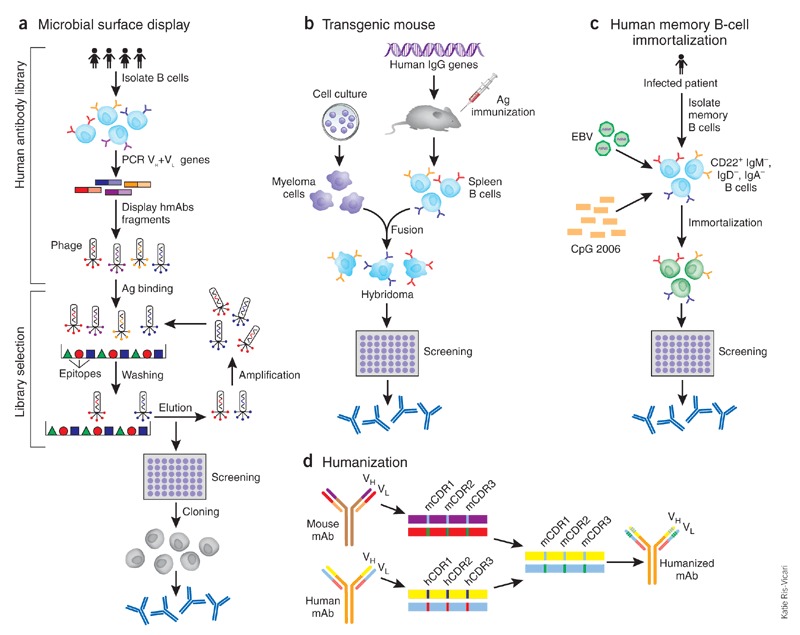
(a) Phage display exemplifies human antibody library display techniques (phage, bacteria, yeast, mammalian cell and ribosome). Three steps are included in this technique: antibody library construction and display onto the phage surface, selection by panning the library against antigen (Ag) targets, and screening for desired specificity. Diverse human immunoglobulin-variable-region gene segments (as scFv or Fab fragments) are amplified from human B cells of immune or non-immune sources to construct the antibody library. The library is then cloned for display on the surface of the phage. Selection against the desired target is then performed using the phage display library; antibodies that do not bind are washed away and the binders are eluted and amplified by infection of Escherichia coli. After several rounds of such selection, desired specificity can be screened using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or techniques such as fluorescent-activated cell sorting (FACS) if a cell-membrane bound protein is the target. Once the desired specificity is obtained, the genes of antibody variable regions can be cloned into whole human IgG expression vectors and transfected into cell lines to produce fully human mAbs (hmAbs). (b) Transgenic mouse. The mouse immunoglobulin genes have been genetically knocked out and replaced with human counterparts. The transgenic mouse will make human antibodies after foreign antigen immunization. The B cells harvested from immunized mice are immortalized by fusion with a myeloma cell line, as in traditional hybridoma technology. The hybridomas are then screened for desired specificity. (c) Memory B-cell immortalization. Memory B cells (CD22+ IgM−, IgD−, IgA−) are isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). They are immortalized by EBV in the presence of a CpG oligodeoxynucleotide and irradiated allogeneic PBMCs. The culture supernatants are then screened directly for specific antibodies. Positive cultures are further cloned by limiting dilution and fully human mAbs can then be produced from the cloned B cells. (d) CDR grafting exemplifies humanization. CDR residues from variable region of a mouse mAb are transferred to human antibody frameworks that have high sequence homology with the mouse counterparts.
Katie Ris-Vicari
