Figure 2. Different interferon (IFN) signalling pathways activated by dsRNA and viruses.
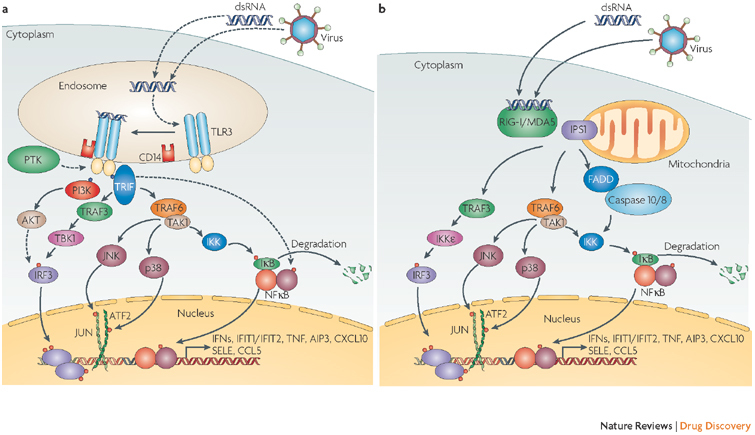
Extracellular double-stranded (ds) RNA or intracellular dsRNA produced during viral replication can activate different signalling pathways triggered by either membrane-bound Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) or cytoplasmic retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I; also known as DDX58) or melanoma differentiation associated protein 5 (MDA5; also known as IFIH1). a | TLR3 recognizes dsRNA in the lumen of the endosome, which causes phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues in TLR3 by an unidentified protein tyrosine kinase (PTK). TLR3 dimerizes, binds to CD14 and activates the signalling complex assembled by TLR adaptor molecule 1 (TRIF). Two major pathways bifurcate from TRIF. One, composed of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) and TANK-binding kinase (TBK1/IKKE), leads to phosphorylation of the transcription factor IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3). IRF3 requires further phosphorylation by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (P13K)/AKT pathway for its full activation, which is initiated by binding PI3K to phosphorylated TLR3. The other branch acts through TRAF6 and transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1; also known as MAP3K7) leading to the activation of nuclear factor-κB (NFκB), JUN and activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2) transcription factors. The activated transcription factors translocate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, bind to the cognate sites in the promoters of the target genes and singly or in combinations induce their transcription. b | The cytoplasmic RNA helicases RIG-I and MDA5 recognize dsRNA or 5′ triphosphorylated single-stranded (ss) RNA and use the mitochondrial membrane-bound protein IFN-β-promoter stimulator 1 (IPS1; also known as VISA) as the specific adaptor. IPS1 functions like TRIF and activates the same transcription factors leading to the induction of similar genes. In addition, they cause apoptosis by activating caspases 8 and 10 through the interaction of FADD with IPS1. Solid arrows denote steps that have been fully delineated, stippled arrows show steps that contain as yet unknown intermediaries. AIP3, atrophin-1 interacting protein 3; CCL5, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5; CXCL10, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10; IFIT1/2, interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1/2; IKK, inhibitor of NFκB kinase; SELE, selectin E (endothelial adhesion molecule 1).
