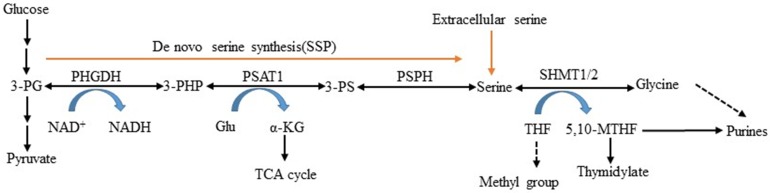
Figure 1.
L-serine synthesis pathway. PHGDH first catalyzes the oxidation of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PG) to 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate (3-PHP), with the coinstantaneous reduction of the cofactor NAD+ to NADH. The subsequent transamination reaction is catalyzed by phosphoserine aminotransferase (PSAT), which uses glutamate (Glu) as a nitrogen donor and thereby converts 3-phosphoserine (3-PS) and α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) into tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Dephosphorylation of phosphoserine via phosphoserine phosphatase (PSPH) produces serine, and then serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) converts serine into glycine and 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-MTHF) via tetrahydrofolate (THF) supplying methyl.