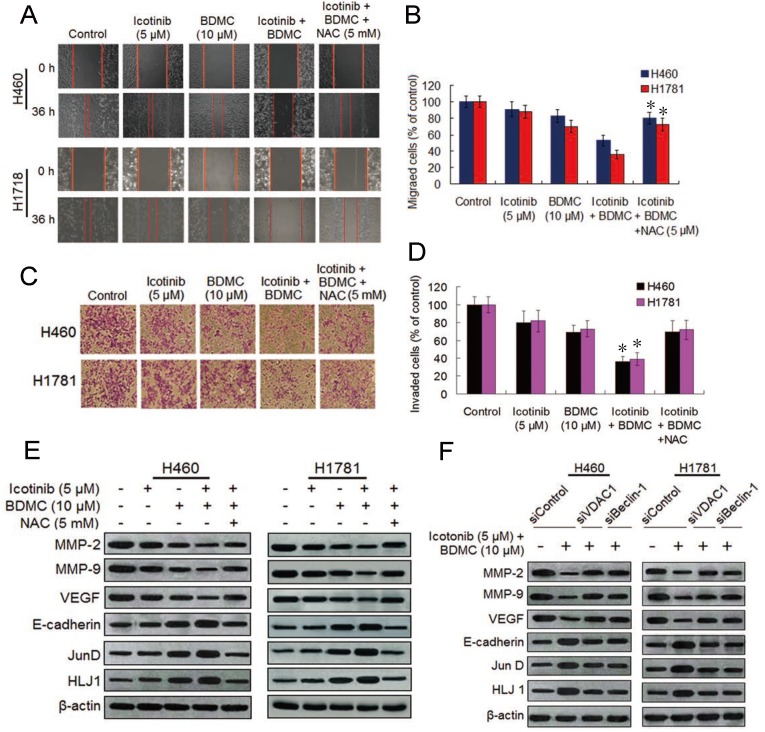
Figure 6.
Icotinib plus BDMC inhibits cell migration and invasion in EGFR-TKI resistant NSCLC cells. (A and B) The effect of icotinib plus BDMC on cell migration was measured using the wound-healing assay. Confluent monolayers of H460 and H1781 cells were scratched, and then treated with icotinib and/or BDMC, or the two combination plus NAC at indicated doses for 36 h. Images were acquired immediately (0 h) and at 36 h after wounding. Cell migrating into the wound area were counted based on the dash line as time zero. The quantity of cell migration to the wound area was defined as 100% in control at 36 h time points. *P < 0.05 versus icotinib + BDMC + NAC, or BDMC. (C and D) The transwell invasion assay was performed to determine the effect of icotinib plus BDMC treatment on cell invasion. After 24 h incubation with or without the indicated concentration of icotinib and/or BDMC, or the two combinations plus NAC, H460 and H1781 cells that had invaded the lower chamber were fixed, stained, and counted using light microscope or fluorescent microscopy-based high content screening system, as described in Materials and Methods. The quantity of invasion cells was defined as 100% in control. *P < 0.05 versus icotinib + BDMC + NAC, or BDMC. (E) H460 and H1760 cells were treated with icotinib and/or BDMC, or the two combinations plus NAC at indicated doses, and then subjected to immunoblot assay to determine the protein expressions as indicated. (F) After transfection with siControl, or siVDAC1, or siBeclin-1, H460 and H1781 cells were treated with icotinib plus BDMC at indicated doses for 48 h, and then subjected to immunblot assay to determine the protein expressions as indicated.