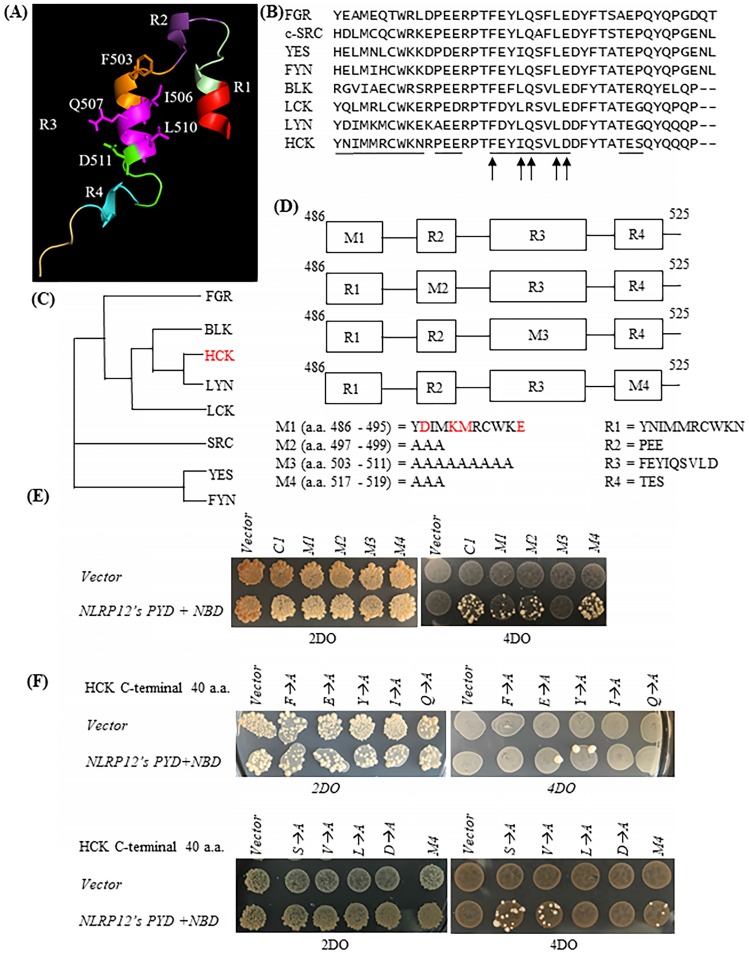
Figure 3.
(A) Structure of the HCK C1 fragment generated by Chimera from the University of California, San Francisco (version 1.13.1), extracted from its structure within the entire HCK protein. HCK C1 fragment was thus divided into four helical domains: R1, R2, R3, and R4. The side chains of amino acids F503, I506, Q507, L510, and D511 are shown. However, it is not clear whether the C1 fragment retains the structural features shown here when it expressed on its own. (B) Primary amino acid sequence alignments showing of the C1 fragments of all members of the c-SRC non-receptor tyrosine kinase family (40 amino acids for HCK, BLK, LCK, and LYN; 42 amino acids for FGR, c-SRC, YES, and FYN). The black lines indicate the R1, R2, R3, or R4 regions. The arrows denote the five critical amino acids for binding of HCK C1 fragment to NLRP12's PYD + NBD. (C) Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship among all of the C1 fragments of the members of the c-SRC family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases. The phylogenetic tree was produced through Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/ clustalo/). HCK is highlighted in red color. (D) Four sets of distinct mutations were made within the HCK C1 fragment. M1: the amino acids in the R1 region were mutated to the amino acids identical to the R1 region in LYN (mutated amino acids are highlighted in red color); M2: the amino acids in the R2 region were all mutated to alanine (Ala); M3: the amino acids in the R3 region were all mutated to Ala; and M4: the amino acids in the R4 region were all mutated to Ala. (E) Yeast did not grow on high stringency 4DO + 3AT plates when HCK C1 fragment with the M3 mutations was co-transformed with NLRP12's PYD + NBD. But yeast can grow on the high stringency 4DO + 3AT plates when the HCK C1 fragment contained either the M1, M2, or M4 mutations, suggesting that the R3 region within the C1 fragment was necessary for binding to NLRP12 NBD + PYD. (E) Yeast did not grow on high stringency 4DO plates when NLRP12's PYD + NBD was co-transformed with HCK C1 fragment with the nucleotides' product that has single Ala substitutions at either F503, I506, Q507, L510, or D511. But yeast grew on high stringency 4DO plates when NLRP12's PYD + NBD was co-transformed with HCK's C1 fragment with the nucleotides' product in which the following amino acids in the R3 region were individually mutated to Ala: E504, Y505, S508, or V509.