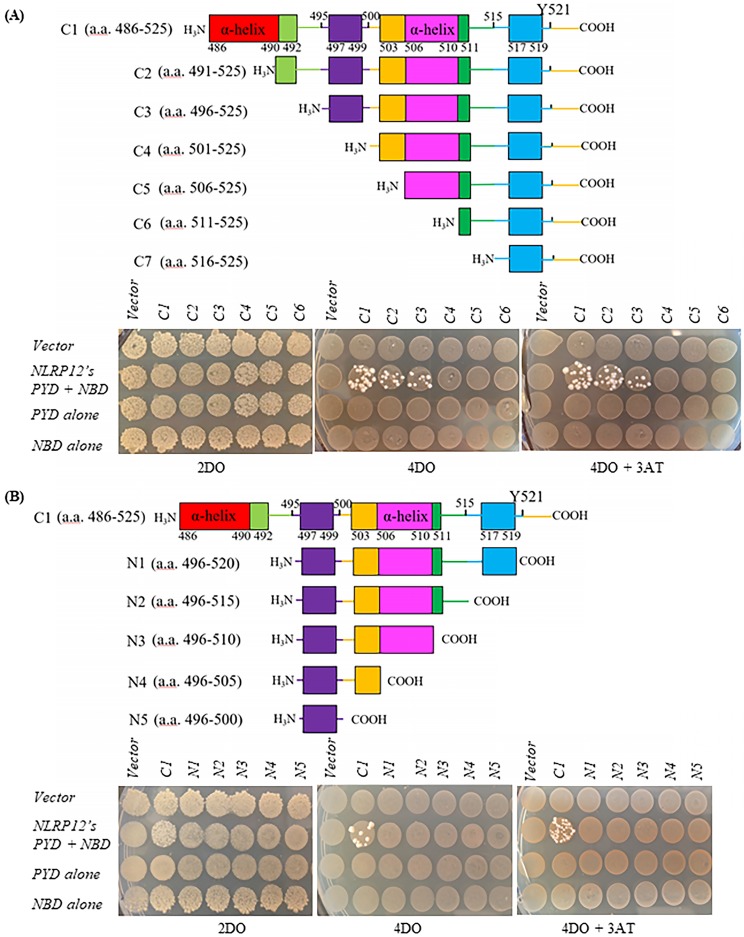
Figure 4.
(A) Top: schematic drawing of HCK truncations comprising the C1 to C7 fragments. Bottom: yeast grew on the high stringency 4DO plates and 4DO +3AT plates when HCK's C-terminal 40 amino acid fragment (C1), HCK's C-terminal 35 amino acid fragment (C2), and HCK's C-terminal 30 amino acid fragment (C3), individually, were co-transformed with NLRP12's PYD + NBD. But yeast did not grow on the high stringency 4DO plates nor 4DO+ 3AT plates when C4 to C7 fragments were co-transformed to with NLRP12's PYD + NBD. The lack of yeast growth upon co-transformation of the C7 fragment and NLRP12 are not shown. (B) Top: schematic drawing of Hck truncations comprising the N1 to N5 fragments. Bottom: yeast grew on the high stringency 4DO plates and 4DO +3AT plates when HCK's C-terminal 40 amino acid fragment (C1) was co-transformed with NLRP12's PYD + NBD (control). But yeast did not grow on the high stringency 4DO plates nor 4DO+ 3AT plates when N1 and N5 fragments were co-transformed with NLRP12's PYD + NBD, suggesting that the very C-terminal 5 amino acids are also necessary for binding of NLRP12. The colored boxes represent different fragments that were deleted each time.