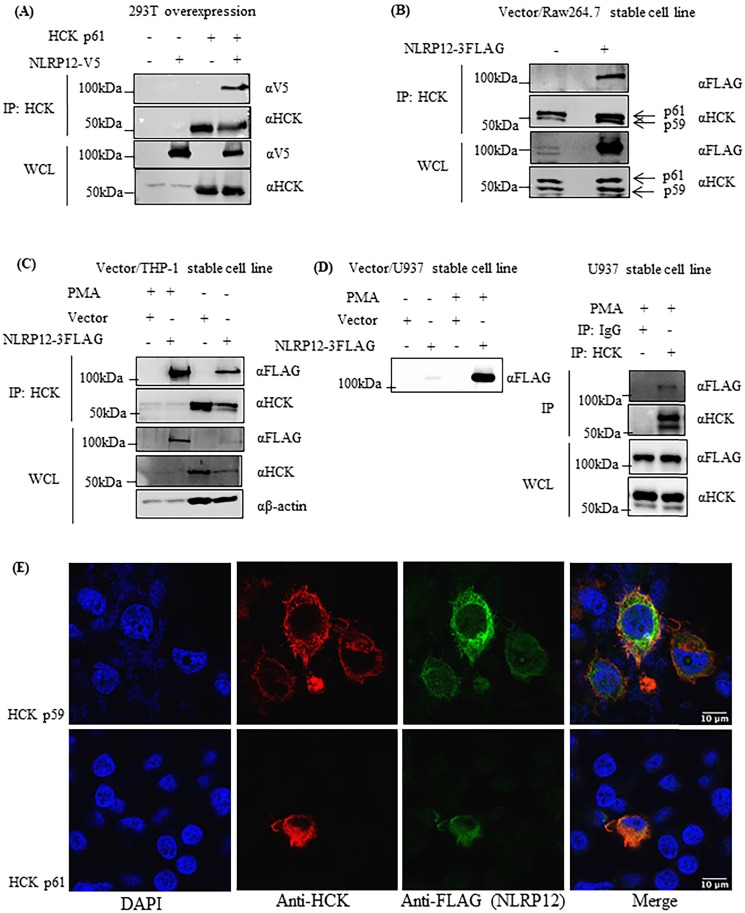
Figure 5.
NLRP12 co-immunoprecipitates with HCK and co-localizes with HCK by immunofluorescence. (A) NLRP12 co-immunoprecipitated with HCK when both proteins were transiently exogenously co-expressed in 293T cells, with NLRP12 having to be expressed as epitope-tagged forms. Cells were lysed using a non-denaturing cell lysis buffer (see Material and Methods). Co-immunoprecipitations were done using a mouse monoclonal anti-HCK antibody followed by protein A/G agarose. The immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. A mouse monoclonal anti-V5 antibody was used for detecting NLRP12-V5, while a mouse monoclonal anti-HCK antibody was used for detecting HCK. The same method was used for experiments shown in (B), (C), and (D). (B) NLRP12 co-immunoprecipitated with endogenous HCK in macrophage-like RAW 264.7 cells, when NLRP12 is exogenously and stably expressed. Arrows show the two isoforms of HCK p59 and p61 that were immunoprecipitated by the anti-HCK antibody, although it is not clear whether NLRP12 co-immunopreciptitated with one form or the other, or both. A mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody was used for detecting NLRP12-FLAG, while a mouse monoclonal anti-HCK antibody was used for detecting HCK. (C) Exogenously and stably expressed NLRP12 co-immunoprecipitated with endogenously expressed HCK in monocyte-like THP-1 cells. In these cells, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) (1µM) was added to enhance the expression of NLRP12 under the PMA-sensitive cytomegalovirus promoter of the NLRP12 plasmid. A mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody was used for detecting NLRP12-FLAG; a mouse monoclonal anti-HCK antibody was used for detecting HCK; and a mouse monoclonal anti- β actin was used as the protein loading control. (D) Left panel shows that NLRP12 was exogenously and stably expressed in lymphoblast-like U937 cells. Right panel shows that NLRP12 co-immunoprecipitated with endogenously expressed HCK in U937 cells after PMA was added to 1µM, as was done for THP-1 cells, to enhance expression of NLRP12. In addition, a mouse monoclonal anti-IgG antibody was used for immunoprecipitation as a negative control. A mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody was used for detecting NLRP12-FLAG, while a mouse monoclonal anti-HCK antibody was used for detecting HCK. (E) Immunofluorescent images showing the colocalization of a cohort of NLRP12 with either HCK p59 or p61. HCK was immunolabeled with a mouse monoclonal anti-HCK antibody, followed by a secondary goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) cross-adsorbed, conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488. For NLRP12, the primary antibody was a rabbit monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody, and the secondary antibody was a goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) cross-adsorbed secondary antibody, conjugated to Alexa Fluor 555. Nuclei were counterstained by DAPI.