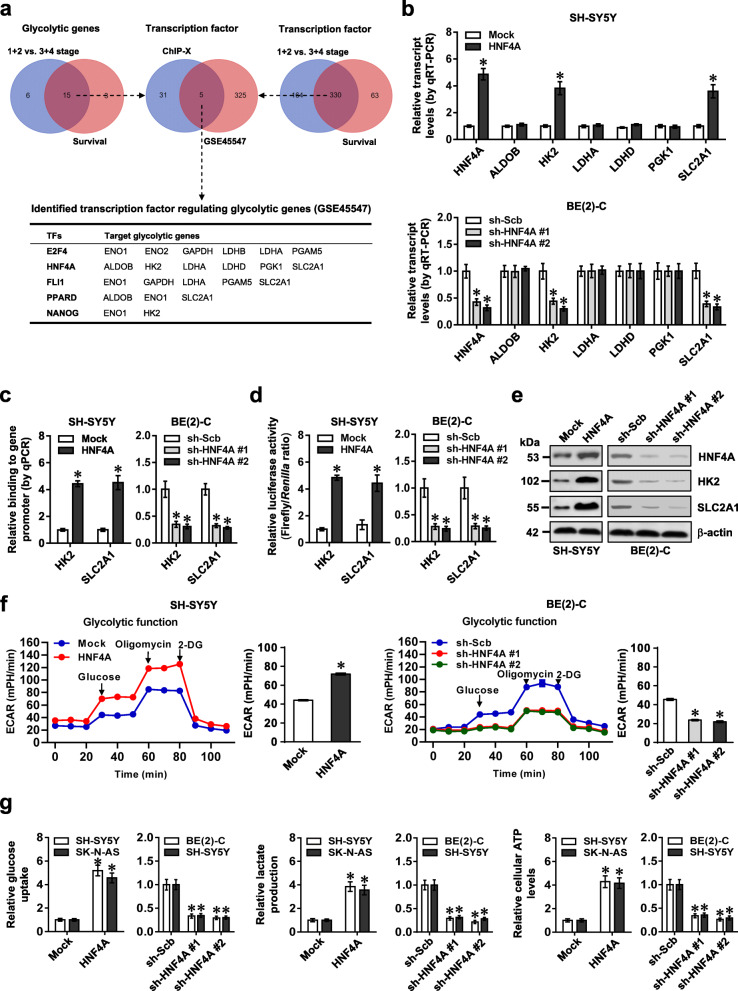
Fig. 1.
Transcription factor HNF4A facilitates glycolytic gene expression and glycolysis of NB cells. a Venn diagram indicating the identification of glycolytic genes (upper left panel) and transcription factors (upper right panel) differentially expressed (P < 0.05) in INSS stages and associated with patients’ survival in 649 NB cases (GSE45547), and over-lapping analysis with potential transcription factors regulating glycolytic genes revealed by ChIP-X program (upper middle panel). The lower panel showing potential transcription factors regulating expression of glycolytic genes. b Real-time qRT-PCR assay (normalized to β-actin, n = 4) revealing the expression of HNF4A, ALDOB, HK2, LDHA, LDHD, PGK1, or SLC2A1 in SH-SY5Y and BE(2)-C cells stably transfected with empty vector (mock), HNF4A, scramble shRNA (sh-Scb), or sh-HNF4A. c ChIP and qPCR assays indicating the binding of HNF4A to promoters of HK2 and SLC2A1 in SH-SY5Y and BE(2)-C cells stably transfected with mock, HNF4A, sh-Scb, or sh-HNF4A (n = 4). d and e Dual-luciferase (d) and Western blot (e) assays showing the promoter activity and expression levels of HK2 and SLC2A1 in SH-SY5Y and BE(2)-C cells stably transfected with mock, HNF4A, sh-Scb, or sh-HNF4A (n = 4). f Seahorse tracing curves (left panel) and ECAR bars (right panel) of SH-SY5Y and BE(2)-C cells stably transfected with mock, HNF4A, sh-Scb, or sh-HNF4A (n = 4), and those treated with glucose (10 mmol·L−1), oligomycin (2 μmol·L−1), or 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG, 50 mmol·L−1) at indicated points. g The glucose uptake, lactate production, and ATP levels in SH-SY5Y, SK-N-AS, and BE(2)-C cells stably transfected with mock, HNF4A, sh-Scb, or sh-HNF4A (n = 4). Fisher’s exact test for over-lapping analysis in a. Student’s t test and ANOVA compared the difference in b–d, f and g. *P < 0.05 vs. mock or sh-Scb. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. (error bars) and representative of three independent experiments in b–g