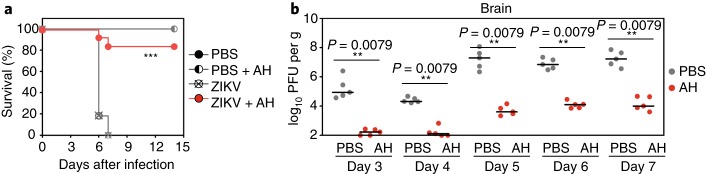
Fig. 2. In vivo efficacy of AH-D peptide in mice.
a,b, Type-I interferon receptor knockout mice (IFN-α/βR–/–) were intravenously infected with 4 × 103 plaque-forming units (PFU) of Zika virus (ZIKV). The infected mice were treated with 25 mg kg–1 AH-D peptide or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) mock on days three to six post-infection. The mice were monitored for survival (a). The levels of infectious virus within the brain (b) were measured on days three to seven post-infection. The AH-D treatment significantly decreased viral loads in serum and various organs, leading to improved survival. Adapted from ref. 2, Springer Nature Ltd.