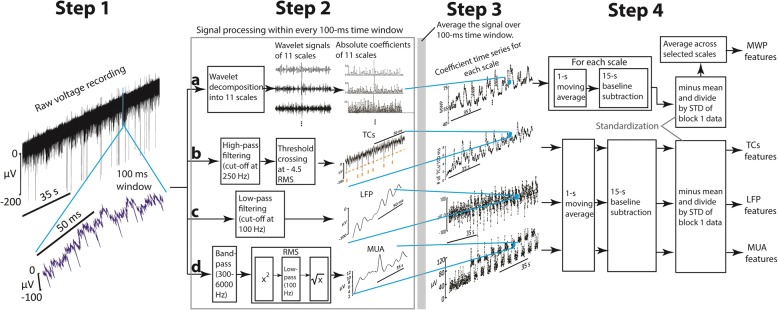
Fig. 2.
Processing of raw signal into different neural features. Step 1: A 100 ms section of neural signal was selected from a larger raw voltage recording. Step 2: Conduct signal processing for this 100 ms raw signal. In method a), raw signal was decomposed into 11 wavelet scales to get the rectified wavelet coefficients of each scale; In method b), a high-pass filter and threshold of - 4.5 times of the RMS value was applied to detect the TCs within this 100 ms section of raw signal; In method c), a low pass filter was applied to get LFP of the raw signal; In method d), band pass filter and customized RMS values were calculated to get MUA of the raw signal. Step 3: The processed signal within this time window were then averaged over this 100 ms, respectively, to compose the related one data point in the averaged larger time series of an entire block. Step 4: Signal smoothing and standardization. To generate MWP feature time series, a 1-s moving average and a 15-s wide mean subtraction were applied to this averaged time series of the entire block. Afterwards, the processed time series were standardized and averaged accordingly across selected scales to produce a new time series for each channel. To generate other feature time series, the processed signal after Step 3 was applied 1-s moving average, a 15-s mean subtraction and standardization, sequentially (Please refer to the Methods section for more details)