Figure 4.
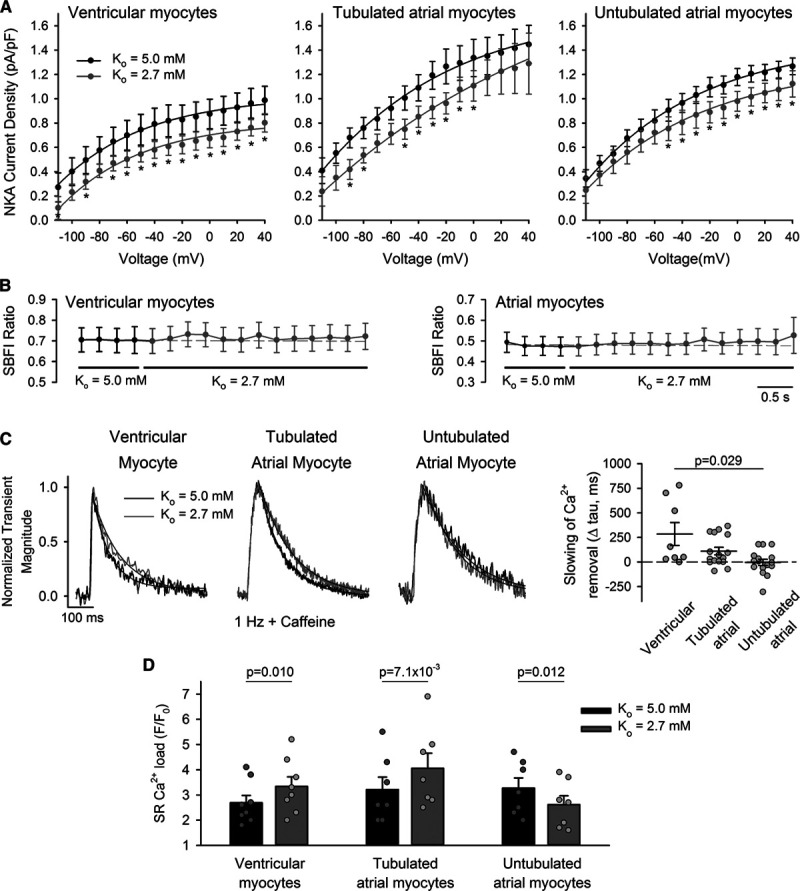
Decreased Na+, K+-ATPase (NKA) activity during hypokalemia inhibits Ca2+ extrusion by t-tubular Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (NCX), elevating sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ content. A, NKA activity was measured during hyperpolarizing voltage ramps and calculated as the K+-sensitive current (see Online Figure I for protocol and representative traces). Hypokalemia induced a modest and similar reduction in NKA current in ventricular myocytes and atrial cells, regardless of the presence of t-tubules (ncells=10, 7, 9; nhearts=4, 4, 5 in ventricular, tubulated atrial, untubulated atrial cells). B, SBFI experiments revealed no change in global cytosolic [Na+] during the protocol (ncells=12, 8; nhearts=4, 4 for ventricular, atrial cells). C, However, tubulated cells showed slowed Ca2+ removal by NCX during hypokalemia, as indicated by the declining phase of Ca2+ transients stimulated in the continuous presence of 10 mmol/L caffeine (change in tau values shown at right, ncells=8, 16; nhearts=3, 5, in ventricular, tubulated atrial cells, P=0.016, 0.011 vs Ko=5.0 by Wilcoxon signed-rank test). No change in Ca2+ removal rate was observed in untubulated atrial cells (ncells=16; nhearts=5; P=0.912). Transient magnitude during Ko=2.7+caffeine: F/F0=1.46±0.07, 1.66±0.12, 1.57±0.08 in ventricular, tubulated, and atrial cells. D, Ventricular cells and tubulated atrial cells exhibited increased SR Ca2+ content during hypokalemia, as assessed by the magnitude of caffeine-induced Ca2+ release (ncells=8, 7, 7; nhearts=6, 6, 5 in ventricular, tubulated atrial, untubulated atrial cells; representative traces illustrated in Online Figure VI). Statistics: (A): 2-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (see Online Table II for full results); (B): Kruskal-Wallis test (difference in medians: P=1.000, 1.000 in ventricular, atrial cells); (C): Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn correction (difference in medians: P=0.023); (D): paired t-test. *P<0.05 vs Ko=5.0.
