Figure 4.
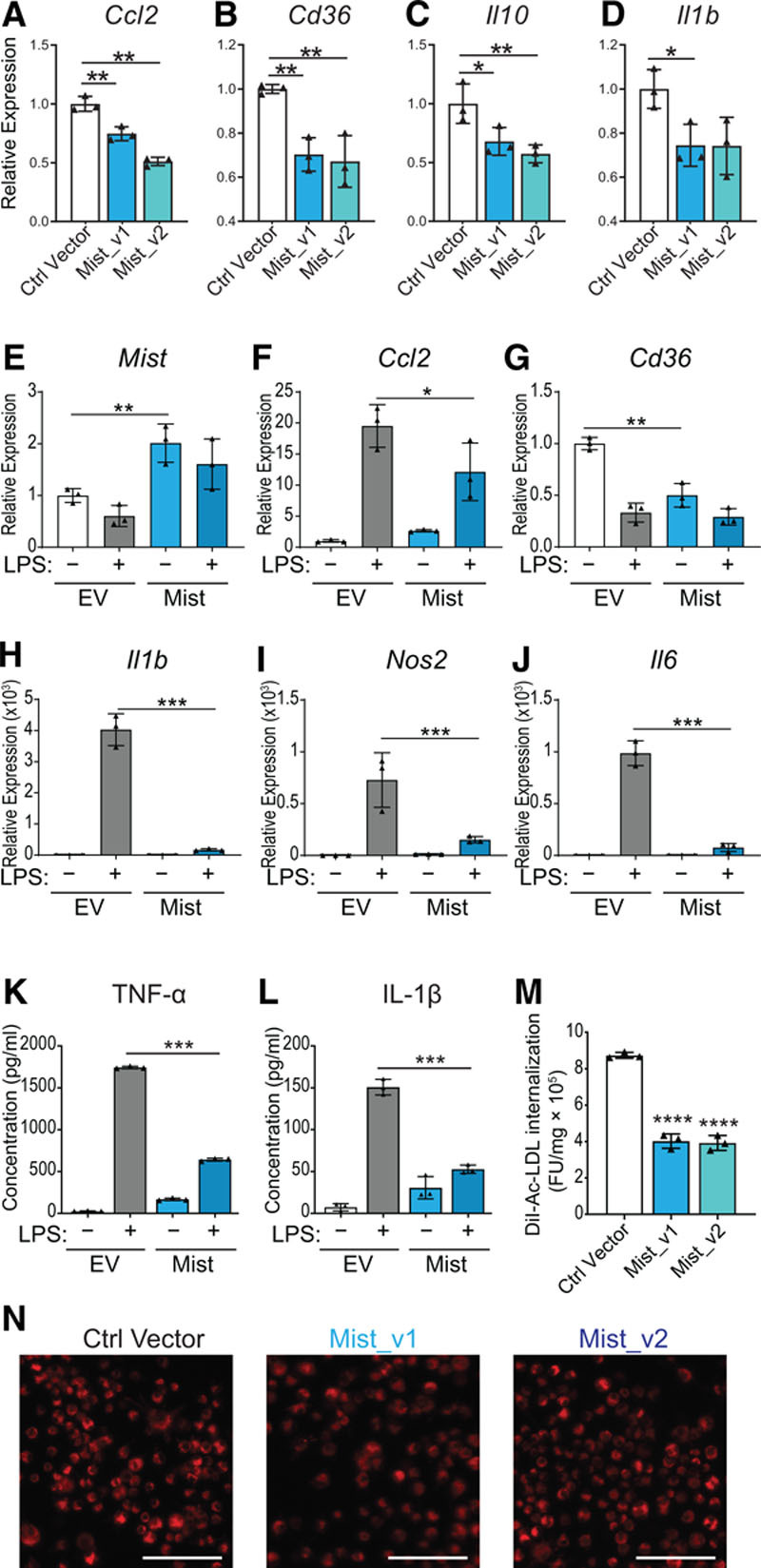
Macrophage inflammation–suppressing transcript (Mist) gain-of-function blunts inflammatory response in macrophages and decreases modified LDL (low-density lipoprotein) uptake. A–D, Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) of indicated genes after Mist transient overexpression in RAW cells. Mist splice variants (v1 and v2) were cloned into pcDNA3.1 expression vectors (Figure IIIC through IIIE in the Data Supplement). Ctrl vector refers to Mist antisense sequence cloned into pcDNA3.1(-) vector, n=3. E–J, Mist overexpression in bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDMs). RT-qPCR of select genes in BMDMs after transfection with pcDNA3.1_Mist_v1 construct (Mist) or empty vector control (EV). Cells were treated with or without LPS (10 ng/mL) 72 h post-transfection, and RNA collected 16 h later, n=3. K, TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor α) and (L) IL (interleukin)-1β levels, analyzed by ELISA, in supernatants from mouse BMDMs transfected with Mist overexpression vector or EV. M, Spectrofluorometric assay of RAW cells stably overexpressing Mist splice variants or Mist antisense sequence (Ctrl Vector), exposed to DiI-ac-LDL (red) for 4 h (n=3). N, Representative images of DiI-ac-LDL internalization in RAW cells. Scale bar represents 50 µm. All bar graphs represent mean values, error bars=SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, and ****P<0.0001 calculated using Fisher least significant difference test on log-transformed expression values (A–J) or Student t test (K–M).
