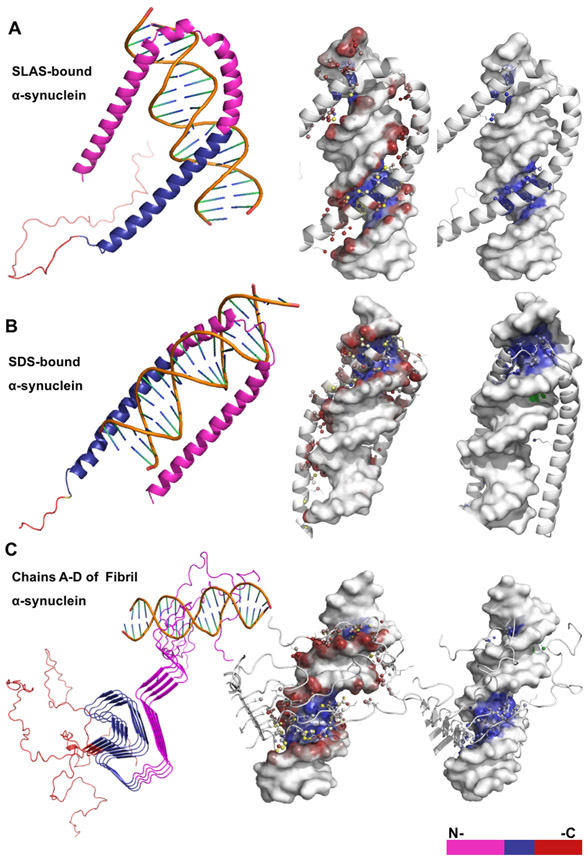
Figure 2. NP-Dock graphical representation of α-helical and β-sheet α-synuclein structures bound to DNA.
Description of protein-DNA complexes (left to right): Protein domains are highlighted; protein residues interacting with either the DNA backbone or base atoms are shown as colored red, blue, or yellow spheres; protein residues interacting with the major or minor DNA grooves are blue or green, respectively. (A) The SLAS-bound α-synuclein structure (PDB:2KKW) contains ~20 predicted binding residues and interacts only with DNA major groove. (B) The SDS-bound α-synuclein structure (PDB: 1X8Q) contains ~23 predicted binding residues and interacts with both the major and minor DNA grooves. (C) The fibril α-synuclein structure (PDB2N0Achain A-D) contains ~29 predicted binding residues that are distributed across structural chains B-D.