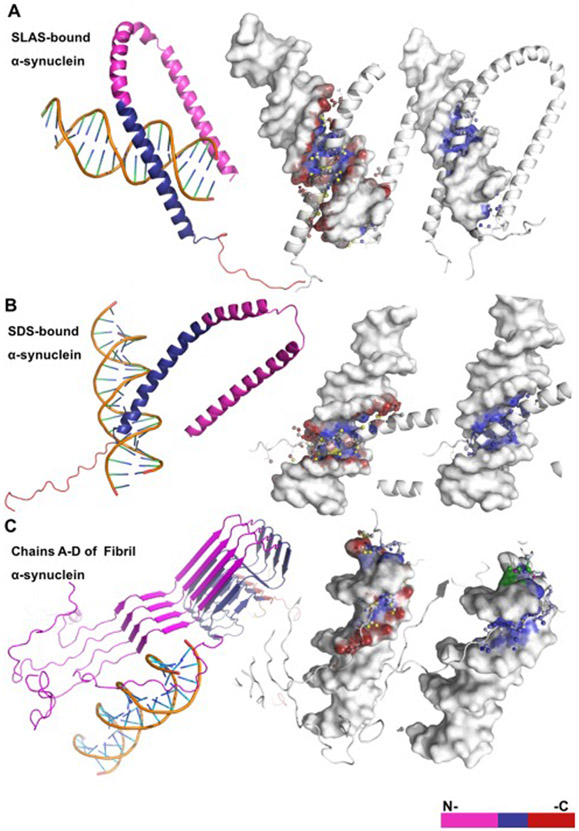
Figure 3. HDOCK graphical representation of α-helical and β-sheet α-synuclein structures bound to DNA.
(A) The anti-parallel α-synuclein structure (PDB: 2KKW) contains ~13 predicted binding residues located mainly within the NAC domain and interacts only with the DNA major groove. (B) The micelle-bound α-synuclein structure (PDB: 1X8Q) contains ~18 predicted binding residues within the NAC and C-terminal domains and interacts only with the DNA major groove. (C) The α-synuclein fibril structure (PDB 2N0A) contains ~14 predicted binding residues that are located within the C-terminal domain and interacts with both the major and minor DNA grooves.