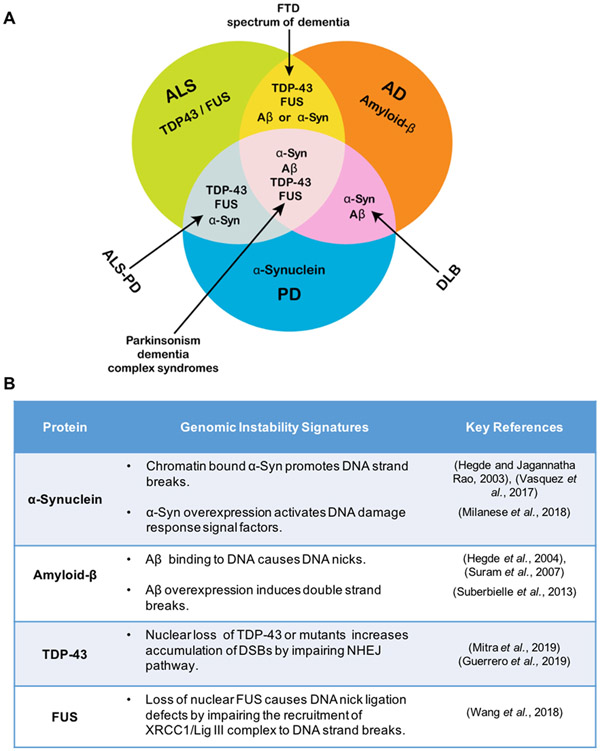
Figure 5. Crosstalk between α-synuclein and other amyloidogenic proteins.
(A) Venn diagram of key amyloidogenic proteins involved in motor- and dementia-related neurodegenerative disorders illustrating the overlapping proteins involved in various disease states. Notably, α-synuclein overlaps with other amyloidogenic proteins, which are also known to induce genomic instability in specific neurodegenerative conditions. In Guamanian ALS/PD, α-synuclein overlaps with DNA repair inhibiting proteins TDP-43 and FUS. In Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB), α-synuclein interacts with DNA damage inducing factor amyloid-β. Complex conditions that are not fully characterized, including Parkinsonism-dementia complex syndromes and the frontotemporal spectrum of dementia may result from the pathological overlap of key amyloidogenic proteins (Bougea et al., 2017; Steele, 2005; Tan et al., 2017). (B) Table indicating key genomic instability signatures of amyloidogenic proteins.