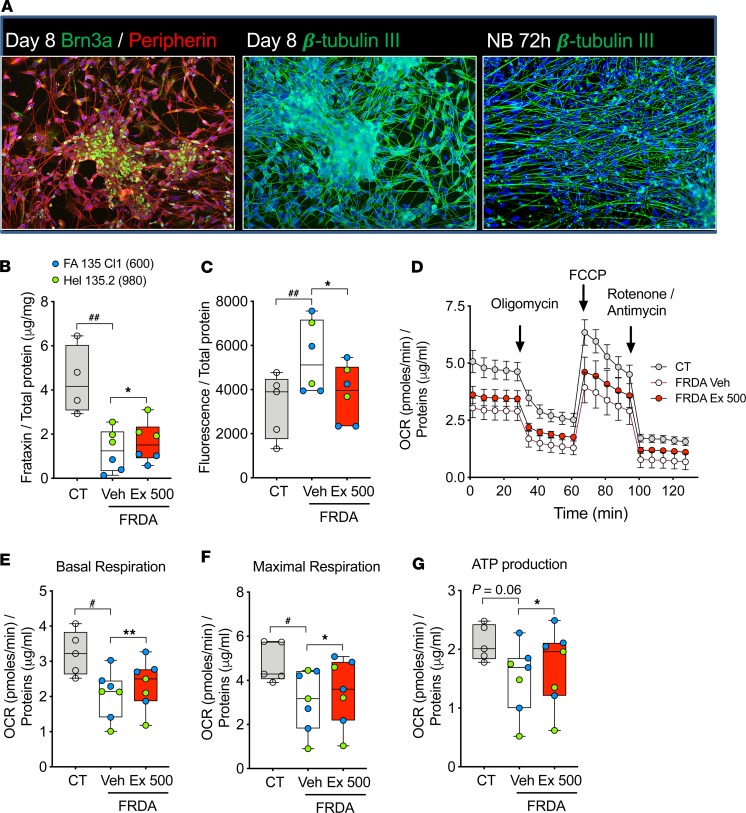
Figure 5. Exenatide alleviates oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in FRDA patients’ iPSC-derived sensory neurons.
Sensory neurons were differentiated from iPSCs from 2 healthy controls (CT1 and CT2) and 2 patients with FRDA (FA135 Cl1 and HEL135.2). At the end of differentiation cells were treated for 72 hours with PBS (Veh) or exenatide (Ex, 500 nM) in neurobasal medium. (A) Representative immunofluorescence of CT1 cells during sensory neuron differentiation (images are representative of 7 similar experiments; more images are shown in Supplemental Figure 7A). Pictures were taken at original magnification ×20. Expression of sensory neuron markers Brn3a and peripherin was examined at day 8 and neuron-specific cytoskeleton marker β-tubulin III at day 8 and after 72-hour culture in neurobasal medium (NB). (B) Frataxin protein expression was analyzed by ELISA and normalized to total protein (n = 4–6 per group). (C) Oxidative stress was measured with hydroxyphenyl fluorescein (HPF) probe. (D–G) Mitochondrial respiration was assessed by XFp Extracellular Flux Analyzer (Seahorse, n = 5–7 per group). (D) Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) profiles of control and FRDA patients’ sensory neurons in basal condition and after injection (arrows) of the ATP synthase inhibitor oligomycin, the mitochondrial uncoupler FCCP, and the metabolic poisons rotenone and antimycin A. (E–G) OCR measures were used to calculate basal respiration, ATP production, and maximal respiratory capacity. The horizontal line in the box corresponds to the median; 25th and 75th percentiles are at the bottom and top of the boxes; and whiskers indicate minimum and maximum values. Data points represent independent experiments. Patients are shown in different colors; the smaller GAA expansion size in FXN is shown in brackets. #P < 0.05, and ##P < 0.01 CT vs. FRDA Veh by unpaired 2-tailed t test; *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01 FRDA Veh vs. FRDA Ex 500 by paired 2-tailed t test.