Figure 1. Intracellular membrane contact sites (MCSs).
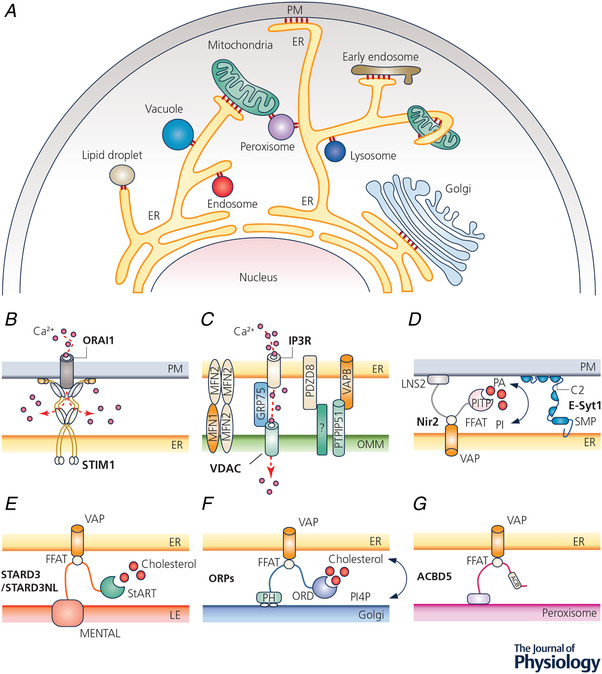
A, diagram depicting MCSs formed between intracellular organelles (red circles). B–G, examples of MCSs and their tentative molecular compositions. B, STIM1–ORAI1 coupling that mediates store‐operated calcium entry at ER–PM junctions; C, the makeup of the ER–mitochondria junctions. IP3R, VDAC, VAPB, PTPIP51, MFN1/2 and PDZD8 are essential for mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and/or the formation of ER–OMM contacts. D–G, lipid transfer by LTPs at MCSs between ER and other organelles. LTPs can establish intermembrane tethering via PH domains, C2 domains, or FFAT‐motif‐dependent interactions with VAP. Abbreviations: ACB, acyl‐coenzyme A binding domain; ACBD5, acyl‐coenzyme A binding domain protein 5; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; E‐syt1, extended synaptotagmin‐1; FFAT, phenylalanine–phenylalanine–acid tract; GRP75, 75 kDa glucose‐regulated proteins; IP3R, inositol 1,4,5‐trisphosphate receptor; LTP, lipid transfer protein; MFN, mitofusin; MEMTAL, MLN64 N‐terminal; Nir2, also called PITPnm1, membrane‐associated phosphatidylinositol transfer protein 1; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; ORD, oxysterol binding protein related domain; PA, phosphatidic acid; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PDZD8, PDZ domain‐containing protein 8; PITP, phosphatidylinositol transfer protein; PH, pleckstrin homology; PM, plasma membrane; PTPIP51, protein tyrosine phosphatase interacting protein 51; STARD3, StAR related lipid transfer domain‐3; STARD3NL, STARD3 N‐terminal like; SMP, synaptotagmin‐like mitochondrial lipid binding protein; STIM1, stromal interaction molecule 1; VAP, vesicle‐associated membrane protein (VAMP)‐associated protein; VDAC, voltage‐dependent anion selective channel.
