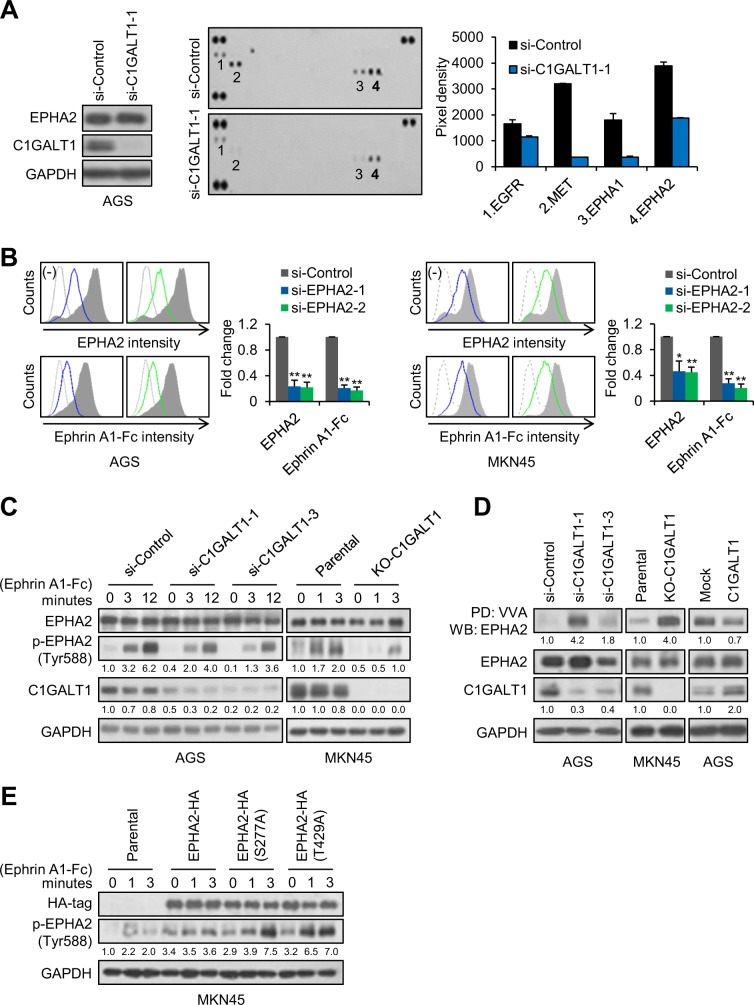
Fig. 4. Impacts of O-glycosylation on Ephrin A1-triggered phosphorylation of EPHA2.
a Phospho-RTK array analysis showing effects of C1GALT1 knockdown on levels of phospho-RTKs in AGS cells treated with Ephrin A1-Fc. Left, western blots showing that AGS cells were knocked down with C1GALT1-specific siRNA. GAPDH was the loading control. Middle, phospho-RTK arrays showing levels of phospho-RTKs in AGS cells transfected with si-Control or si-C1GALT1-1. The cells were serum-starved for 24 h and subsequently treated with 0.2 µg/ml of Ephrin A1-Fc for 3 min. Right, quantification of phospho-RTK levels. b EPHA2 was the predominant EPH receptor for Ephrin A1-Fc in AGS (left panel) and MKN45 (right panel) cells. Cells were knocked down by two independent si-RNAs against EPHA2 and then stained with anti-EPHA2 antibody or Ephrin A1-Fc by flow cytometry. Representative images and their statistical analyses were shown from at least three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. c C1GALT1 knockdown or knockout decreased phosphorylation of EPHA2 at Tyr588 in AGS and MKN45 cells. Cells were treated with Ephrin A1-Fc for different times as indicated. Western blots showing expression of EPHA2, p-EPHA2 (Tyr588), C1GALT1, and GAPDH. Relative signal intensities were quantified by ImageJ and shown below the protein bands. Representative results from three independent experiments were shown. d C1GALT1 could modify the Tn antigen expression on EPHA2 in AGS and MKN45 cells. EPHA2 in cells was pulled down (PD) using VVA agarose beads and then western blotted (WB) for EPHA2. Expression of EPHA2, C1GALT1, and GAPDH in whole lysates was also shown. Representative results from three independent experiments were shown. e Mutations in O-glycosylation sites, S277 and T429, on EPHA2 modulated phosphorylation of EPHA2. S277 and T429 on human EPHA2 were mutated to Ala (A) using site-directed mutagenesis kit. Parental MKN45 cells were transfected with wild-type EPHA2-HA, EPHA2(S277A)-HA mutant, or EPHA2(T429A)-HA mutant. The cells were treated with Ephrin A1-Fc for different times as indicated. Western blots showing ectopic expression of HA-tagged EPHA2, p-EPHA2 (Tyr588), and GAPDH. Representative results from three independent experiments were shown.