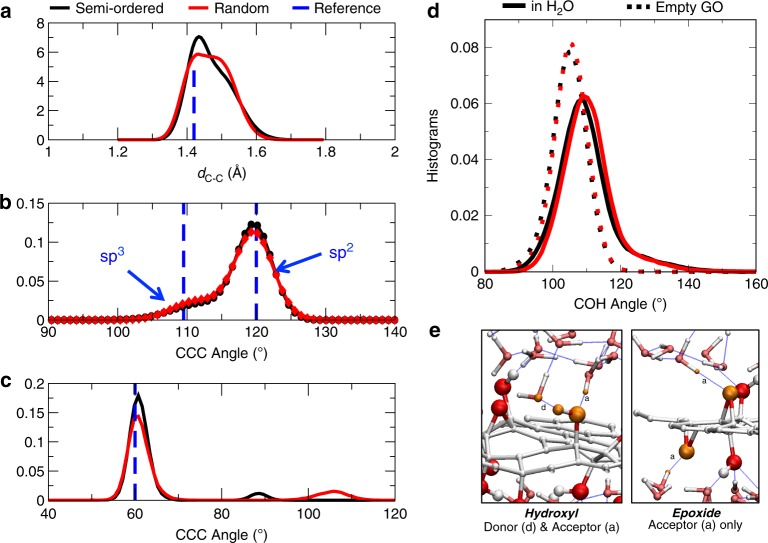
Fig. 2. Structural properties of graphene oxide.
Histograms of the C–C distance dC–C (a), the angle (b), and the angle (c) for semiordered (black) and random (red) graphene oxide models. Blue dashed lines correspond to the values in reference systems: dC–C = 1.42 Å in graphene, , , and for epoxide. d Histogram of the angle for the GO in vacuum (dashed lines) and GO solvated in water (solid lines). e Snapshots of the different H bonds (visualized as blue dashed lines) types classified in Table 3. The atoms of each type of chemical function (hydroxyl group or epoxide) involved in the H bonds between the surface and H2O are highlighted in orange.