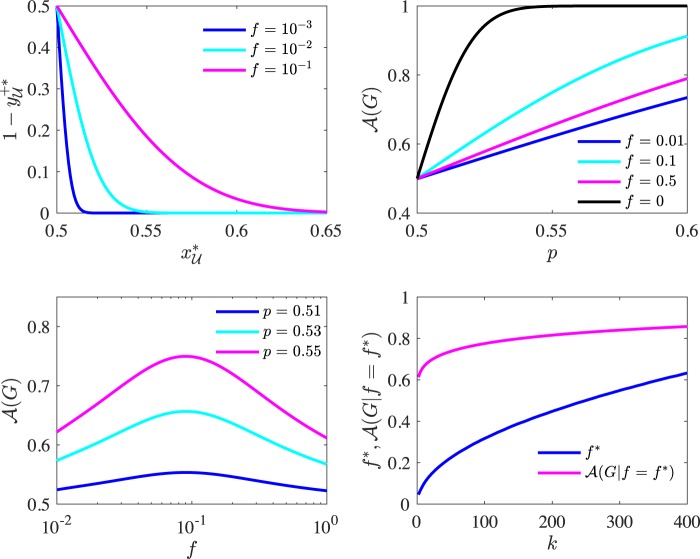
Figure 4.
(Top left panel) Polarization of the unbiased agent population as a function of the average signal mix in the steady state calculated as /2, with given by Eq. (5) . (Top right panel) Expected accuracy (Eq. (6)) as a function of the initial signals’ informativeness . (Bottom left panel) Expected accuracy (Eq. (6)) as a function of the fraction of biased agents. (Bottom right panel) Behaviour of the accuracy-maximizing value and of the corresponding accuracy as functions of . In the first three panels the model’s parameters are , , , while the parameters in the last panel are , , . In all cases we assume without loss of generality.