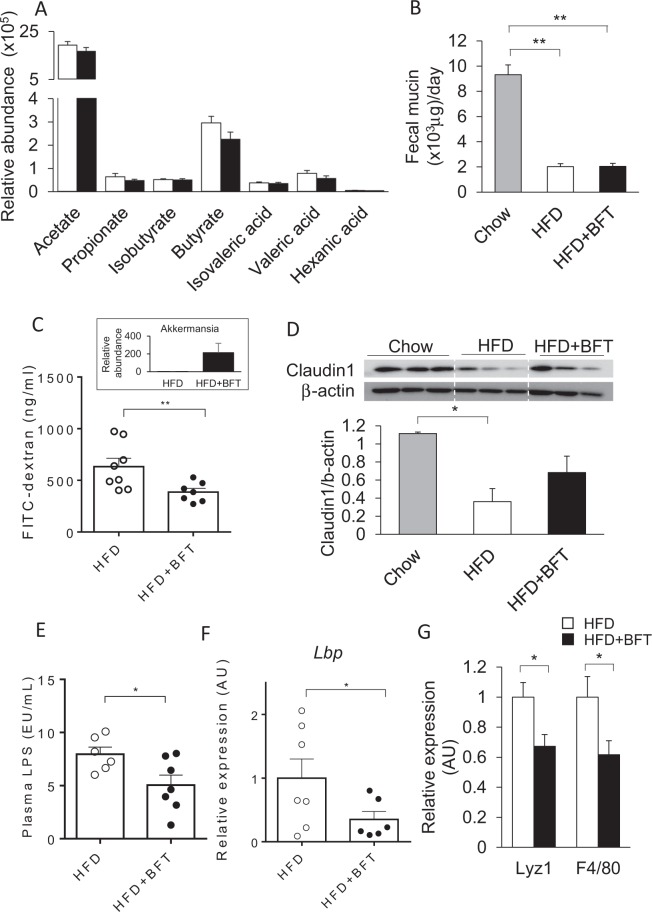
Figure 3.
BFT increases tight-junction related protein in the colon and prevents from metabolic endotoxemia in HF-fed mice. (A) Relative short-chain fatty acid levels in the cecum of HFD (white) or HFD + BFT (black). (B) Fecal mucin content in mice treated either chow, HFD or HFD + BFT. (C) FITC levels in serum of mice after gavage administration of FITC-dextran. The Figure in the upper square is relative Akkermansia DNA levels of mice on a HFD or HFD + BFT used for the experiments (n = 7–8). (D) Western blots for claudin1 in the colon of mice on a chow or an HFD with or without BFT (18 weeks of age, 12 weeks on the HFD, 8 weeks on BFT) and quantitation of claudin1 protein normalized to β-actin (n = 3 per group). (E) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels in serum of mice fed on an HFD with either saline or BFT for 12 weeks (n = 6–7). (F) Lbp mRNA levels in the liver (n = 7). (G) Lyz1 and F4/80 mRNA levels in the colon (n = 8–13). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01, by unpaired, 2-tailed t test for (A,C,E,F,G) or ANOVA, followed by Turkey-Kramer post-hoc for (B,D).