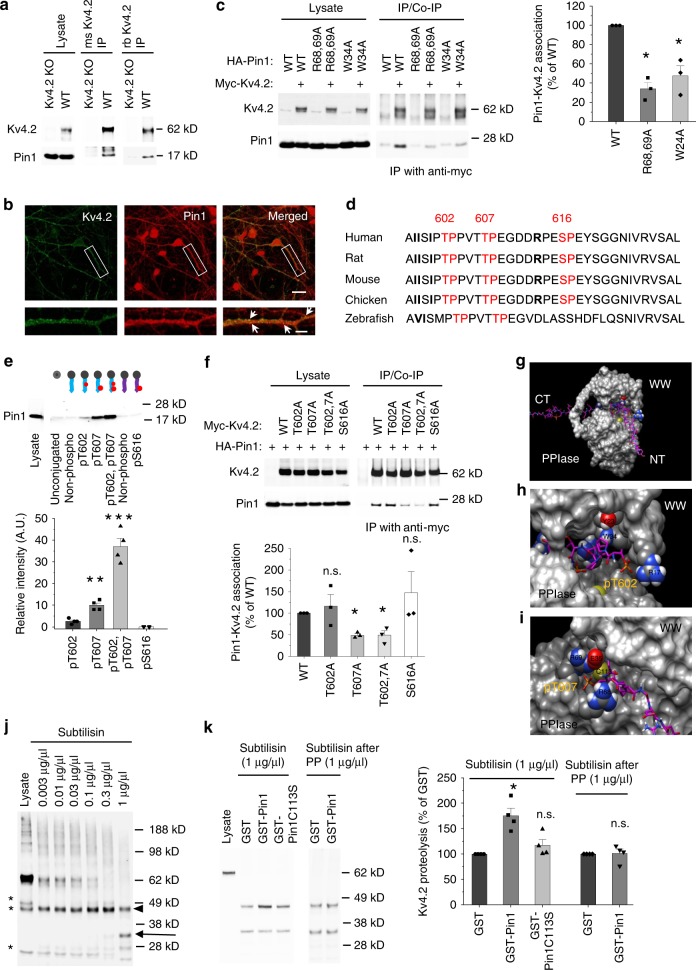
Fig. 1. Pin1 binds to Kv4.2 at pT607 and elicits structural rearrangements in Kv4.2.
a Pin1 co-immunoprecipitated with Kv4.2 in mouse brain lysates. Forebrain lysates from WT and Kv4.2 KO were immunoprecipitated with mouse (ms) or rabbit (rb) anti-Kv4.2 antibodies. Both total lysates and immunoprecipitates were blotted with anti-Kv4.2 or Pin1 antibodies. Data from three independent experiments. b Cultured hippocampal neurons (DIV 10) were immunostained with anti-Pin1 along with anti-Kv4.2. Pin1 co-localized with Kv4.2, indicated with arrows. Scale bars: 20 μm top panels, 5 μm bottom. Data from four coverslips in two independent experiments. c, Pin1 mutants reduced Pin1-Kv4.2 binding. Myc-Kv4.2 was co-transfected alongside HA-Pin1 with or without WW (W34A) or PPIase domain (R68, R69A) point mutants into HEK-293T cells. Kv4.2 was immunoprecipitated from detergent lysates with anti-Myc antibody. Samples were analyzed by western blotting with anti-HA and anti-Myc antibodies. n = 3 each group. d Alignment of Kv4.2 C-terminal sequences from various species. The putative Pin1 binding site is conserved. Bold residues show preferred Pin1 binding context. e Pin1 selectively binds to the phosoho-T607-containing Kv4.2 peptide. Synthetic Kv4.2-peptides were conjugated to Affi-Gel 15 Sepharose beads and incubated with lysate from HA-Pin1 transfected HEK-293T cells. n = 4 each group. f Kv4.2 T607A mutation significantly reduced Pin1 binding. HA-Pin1 and Myc-Kv4.2 mutants were co-transfected into HEK-293T cells. Pin1 co-immunoprecipitation with Kv4.2 was assayed. Kv4.2 T607 is required for Pin1 binding. n = 3 each group. g Molecular modeling of Kv4.2 phospho-peptide binding to Pin1. h Highlight of Kv4.2 pT602 peptide binding to the Pin1 WW domain. i Highlight of Kv4.2 pT607 peptide binding to the Pin1 PPIase domain. j Dose-dependent proteolysis of Kv4.2 by subtilisin. Asterisk, non-specific bands; arrowhead, 47kD band; arrow, 33kD band. Data repeated in two independent experiments. k Pin1 blocked Kv4.2 subtilisin digestion while Pin1C113S (an isomerase dead mutant) did not. Pin1 block was lost when Kv4.2 was dephosphorylated by Lambda protein phosphatase (PP). Quantification of the 47kD degradation fragment. n = 4 each group. Data was repeated in four independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, Paired t-tests.