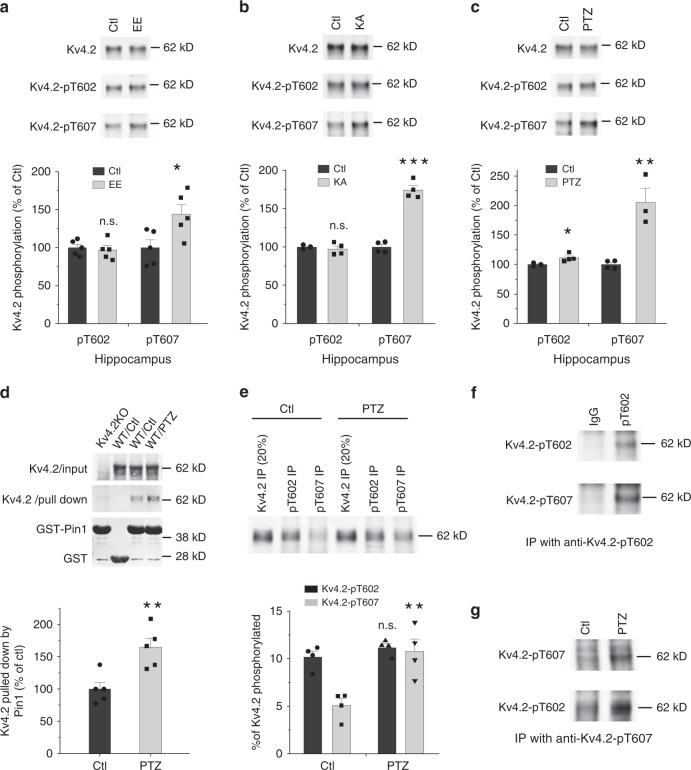
Fig. 2. Enriched novel environment exposure and seizure induce Kv4.2 phosphorylation at a Pin1 binding site.
a Enriched novel environment (EE, 1 h) induces phosphorylation of Kv4.2 at Thr607 but not Thr602 in mouse hippocampus. n = 5 in each group. T-test, *p < 0.05. b Kainic acid-induced seizure (25 mg/kg, i.p., 15 min) induces phosphorylation of Kv4.2 at Thr607 but not Thr602 in mouse hippocampus. n = 4 in each group. T-test, ***p < 0.001. c PTZ-induced seizure (50 mg/kg, i.p., 15 min) induces phosphorylation of Kv4.2 at Thr607 and Thr602 in mouse hippocampus. n = 4 in each group. *p < 0.05, T-test, **p < 0.01. d PTZ-induced seizure increases Pin1 binding to Kv4.2. GST or GST-Pin1-linked beads were incubated with brain lysates from mice subjected to saline or PTZ administration. n = 5 in each group. T-test, **p < 0.01. e Mouse brain lysates from WT mice w or w/o PTZ administration (50 mg/kg, i.p., 15 min) were incubated with excess anti-Kv4.2, anti-Kv4.2-pT602 or anti-Kv4.2-pT607 antibodies. Immunoprecipitation (IP) samples were blotted with Kv4.2 antibody. In WT mouse brains, pT607 Kv4.2 is almost half as abundant as pT602. However, PTZ administration increased the amount of pT607 until it reached a similar level as pT602. n = 4 for each group. T-test, **p < 0.01. f Mouse brain lysates from WT mice were incubated with excess anti-Kv4.2-pT602 or normal IgG antibodies. Immunoprecipitation (IP) samples were blotted with anti-Kv4.2 pT607 antibody. pT602 and pT607 dual phosphorylation was observed in mouse brain. Data was repeated in two independent experiments. g Mouse brain lysates from WT mice w or w/o PTZ administration (50 mg/kg, i.p., 15 min) were incubated with excess anti-Kv4.2-pT607 antibody. IP samples were blotted with anti-Kv4.2 pT602 antibody. PTZ-induced seizure increases the dual phosphorylation of T602 and T607 in mouse brain. Data was repeated in two independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.