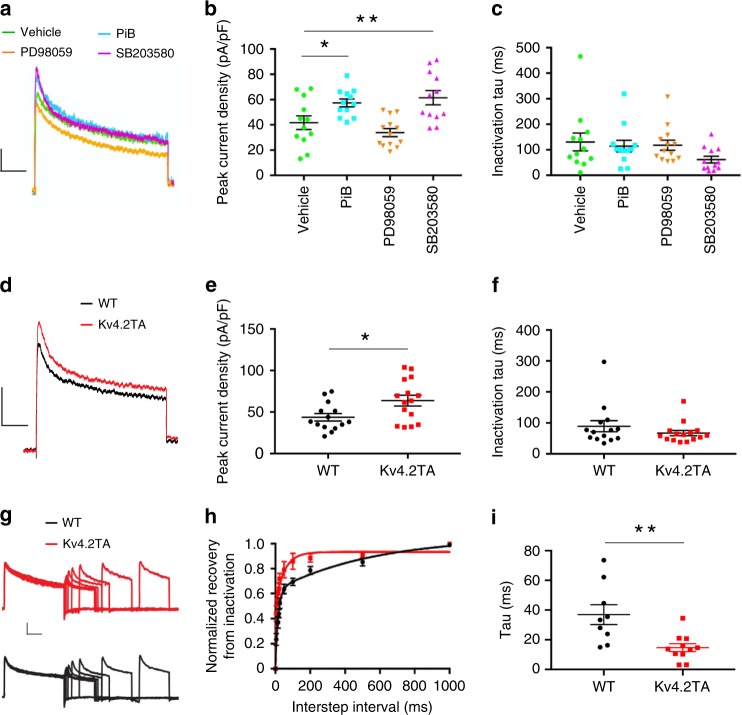
Fig. 6. P38-Pin1-Kv4.2 pathway regulates A-current.
a–c IA recorded from outside-out somatic patches from CA1 pyramidal cells from WT mice. a, Trace of transient IA. inactivating IA was isolated by subtracting total K+ measured from a step to +40 mV from a −120 mV pre-pulse from a subsequent step to +40 mv from −30 mV. Scale: 10 pA/100 ms. b IA density in outside-out patches is significantly increased with PiB (n = 12) or SB203580 (n = 12) but not PD98059 (n = 13), ordinary one-way ANOVA (two-tailed), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. c No significant difference in decay kinetics was observed among the drug treatments and vehicle control, Kruskal–Wallis test (two-tailed), p > 0.05. d Trace of transient IA in WT and Kv4.2TA mice. e IA density in outside-out patches is significantly increased in Kv4.2TA mice (n = 15) relative to WT (n = 14), two-tailed unpaired T-test, *p < 0.05. f No significant difference in decay kinetics was observed between Kv4.2TA and WT, two-tailed Mann–Whitney test, p > 0.05. g–i IA recovery from inactivation. g Sample traces of IA recovery from inactivation in Kv4.2TA and WT. Scale: 20 pA/200 ms. h Normalized recovery curves from Kv4.2TA (n = 11) shows faster recovery relative to WT (n = 9). i Single-exponentials fitted to normalized recovery curves yielded significantly reduced tau in Kv4.2TA relative to WT, unpaired two-tailed T-test. **p < 0.01. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.