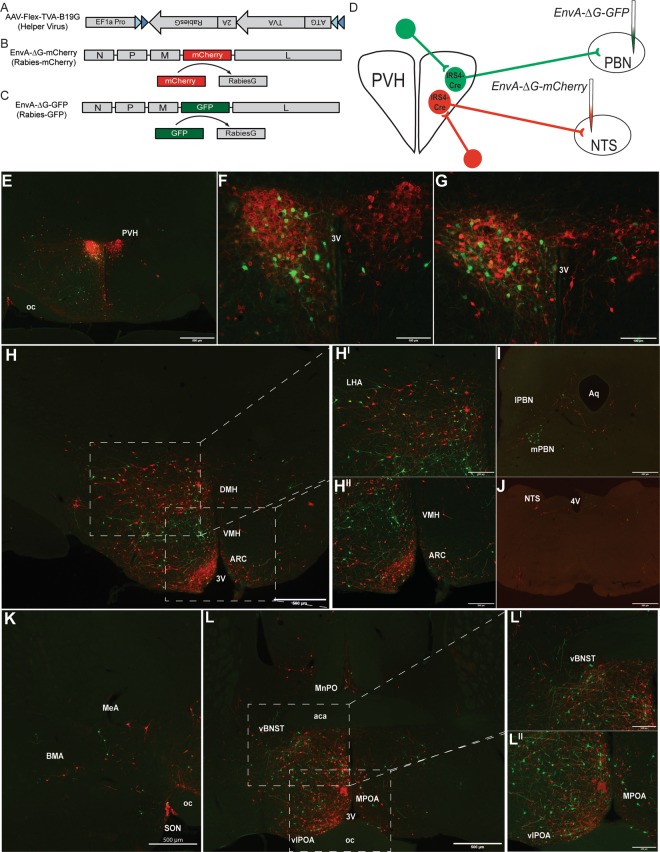
Figure 4.
Identification of monosynaptic inputs to NTS-projecting or PBN-projecting IRS4PVH neurons using modified rabies virus. A Cre-dependent helper virus construct (AAV-Flex-TVA-B19G) is used to insert rabies B19 glycoprotein (B19G) and the TVA receptor in IRS4PVH cell bodies and terminals. Modified rabies virus expresses a fluorescent tag (mCherry, B; GFP, C) instead of B19G. After initial infection with helper virus, rabies-mCherry is injected at one projection site (NTS), whereas rabies-GFP is injected at another (PBN) in the same mouse (D). IHC for mCherry and GFP identify largely non-overlapping NTS-projecting and PBN-projecting IRS4PVH neurons, respectively (E–G). Sites upstream of both NTS and PBN-projecting IRS4PVH neurons include the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA, H), supraoptic nucleus (SON, K), amygdala (K), bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST, L), and the preoptic area (POA, L). The ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) is upstream of PBN-projecting IRS4PVH neurons (HII, green), whereas both the arcuate nucleus (ARC, HII, red) and PBN (I, red) are upstream of IRS4PVH neurons projecting to the NTS. Glial damage represents injection site in the PBN (I, green) and NTS (J, red). 3 V = third ventricle, oc = optic chiasm, MeA = medial amygdala, BMA = basomedial amygdala, vBNST = ventral BNST, vlPOA = ventral lateral POA, MPOA = medial POA, MnPO = median preoptic nucleus, aca = anterior part of anterior commissure, DMH = dorsomedial hypothalamus, aq = aqueduct, 4 V = fourth ventricle.