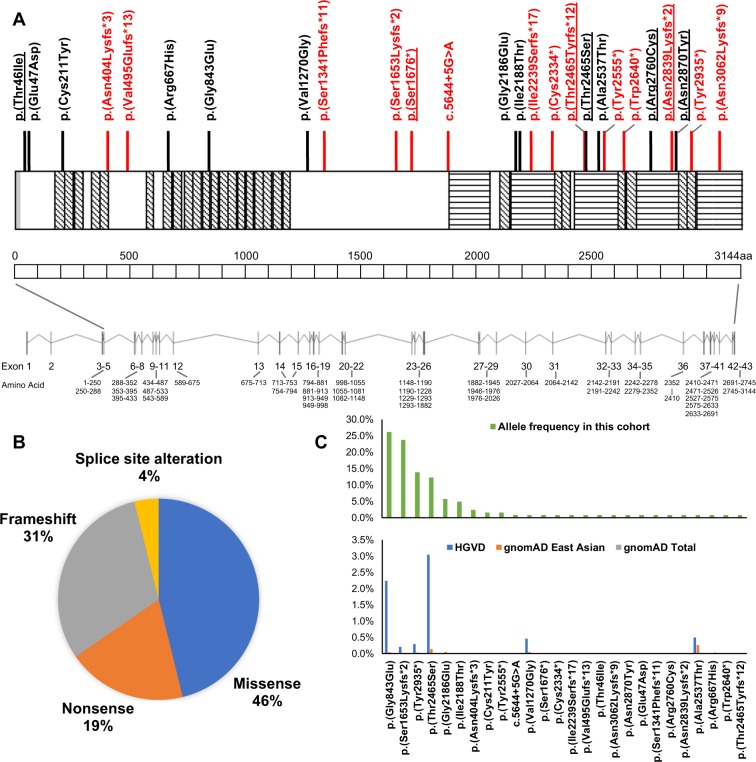
Figure 2.
EYS variants detected in a Japanese cohort with inherited retinal disease (IRD). (A) A schematic genetic and protein structure of EYS and the location of the detected variants in this study. The EYS gene (ENST00000503581.5) contains 43 exons. Exons 4 to 43 encode a 3144-amino acid protein containing 27 epidermal growth factor-like domains (highlighted with diagonal lines) and five laminin G-like domains (highlighted with horizontal lines) as well as one N-terminal signal peptide (highlighted with grey). Truncating variants (nonsense, frameshift, and splice site alteration) are shown in red, and missense variants are shown in black. Novel variants identified in this study are underlined. (B) Distribution of the types of the detected variants. In total, 26 variants were identified, including twelve missense variants (46%), eight frameshift variants (31%), five nonsense variants (19%) and one splicing site alteration variant (4%). (C) Allele frequency (AF) of the detected variants in this EYS-RD cohort and in the general population presented in public databases. Top: The AF in this EYS affected cohort. c.2528 G > A (p.(Gly843Glu)), c.4957dupA (p.(Ser1653Lysfs*2)), c.8805 C > A (p.(Tyr2935*)) and c.7394 C > G (p.(Thr2465Ser)) are the four most prevalent variants, with AFs of 26.23%, 23.77%, 13.93%, and 12.30%, respectively. Bottom: The AF in the general population in the two public databases: the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD; a database for the ethnic and the total general population) and the Human Genetic Variation Database (HGVD; a database for the Japanese general population). The AF of the four most prevalent variants provided by the HGVD/gnomAD East Asian/gnomAD total databases was 2.25%/0.04%/0.00%, 0.21%/0.01%/0.00%, 0.29%/0.03%/0.00%, and 3.05%/0.15%/0.01%, respectively, for c.2528 G > A (p.(Gly843Glu)), c.4957dupA (p.(Ser1653Lysfs*2)), c.8805 C > A (p.(Tyr2935*)) and c.7394 C > G (p.(Thr2465Ser)).