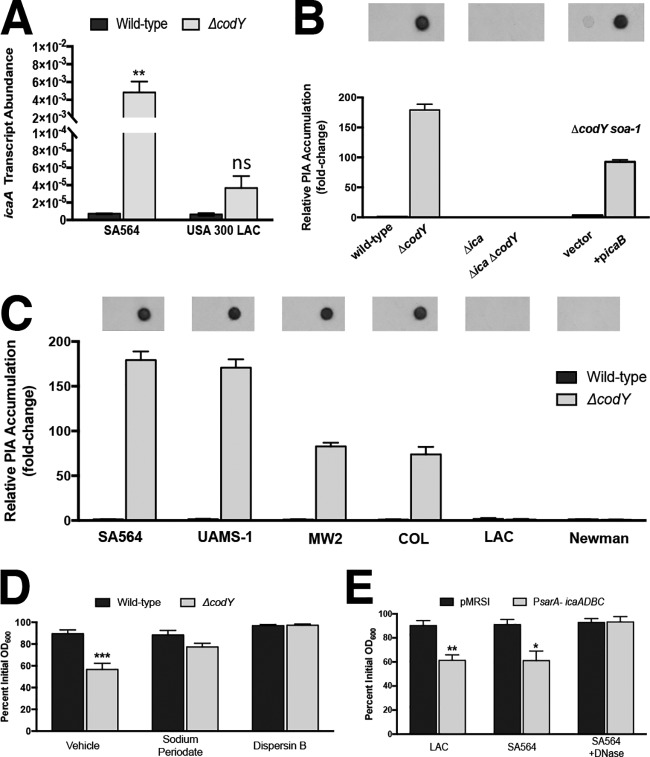
FIG 6.
eDNA-based cell aggregation is dependent on the production of PIA in ΔcodY mutant cells. (A) SA564 and LAC cells were grown to exponential phase aerobically in TSB, and icaA transcript copy numbers in wild-type and ΔcodY mutant cells were determined by qRT-PCR. Data were normalized to rpoC transcript copy number. (B and C) Quantification of cell-associated PIA detected by immunoblot analysis using densitometry for SA564 or isogenic mutants (B) or the wild type and codY-null mutant of the indicated strains (C) obtained from cell pellets grown aerobically for 3 h in tryptic soy broth. When necessary, samples were diluted to avoid membrane saturation. (D) SA564 and ΔcodY mutant cells were grown aerobically in TSB containing sodium metaperiodate (40 μg ml−1) or dispersin B (5 μg ml−1), and aggregation was assessed using the settling assay. (E) Wild-type SA564 and LAC cells constitutively expressing icaADBC under the control of the sarA P1 promoter were grown planktonically in tryptic soy broth, and a settling assay was used to assess aggregation. SA564 was additionally cultured in the presence of DNase I (200 U ml−1). Data indicate the mean ± SEM values from at least three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (using Student’s t test comparing the ΔcodY mutant to the wild type for each condition in panels A, D, and E). ns, not significantly different. Error bars are plotted for all data; in some cases, they are too small to see.