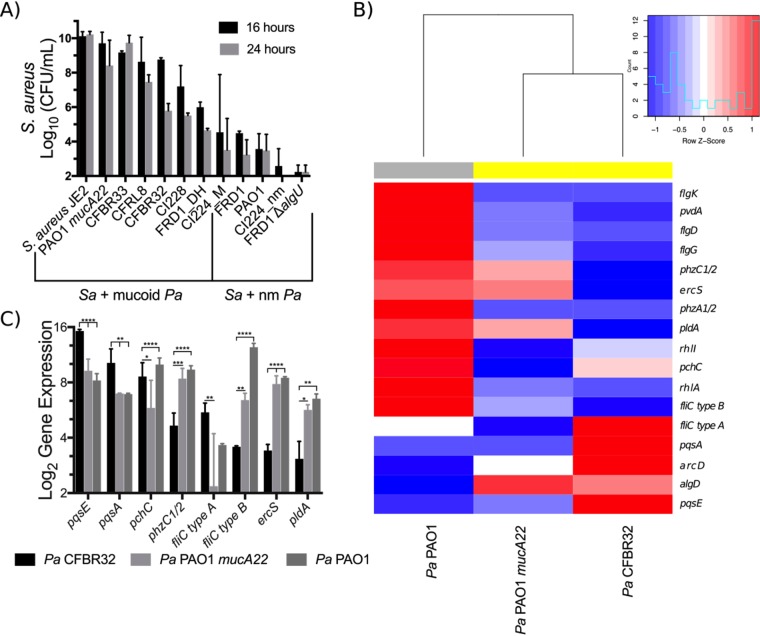
FIG 8.
Mucoid clinical isolates have various effects on S. aureus in coculture. (A) S. aureus JE2 viable counts after 16 and 24 h of coculture in flasks with shaking at 225 rpm in TSB with P. aeruginosa clinical isolates. nm, nonmucoid. (B and C) Log2 transformation of Nanostring counts normalized to values for positive controls and three housekeeping genes (rpoD, ppiD, and fbp) for the indicated transcripts for the clinical isolate P. aeruginosa CFBRPA32 (a “mucoid killer”), mucoid laboratory strain P. aeruginosa PAO1 mucA22, and wild-type laboratory strain P. aeruginosa PAO1 after 24 h of culture in flasks with shaking at 225 rpm in TSB. Data are from two biological replicates per strain. Gene expression was analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. (B) Heat map and dendrogram of all genes significantly differentially regulated between any two strains. Expression values are displayed as within-row z-scores. Yellow indicates mucoid strains, and gray indicates nonmucoid strains. (C) All genes significantly differentially regulated between P. aeruginosa CFBRPA32 and P. aeruginosa PAO1 mucA22. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.