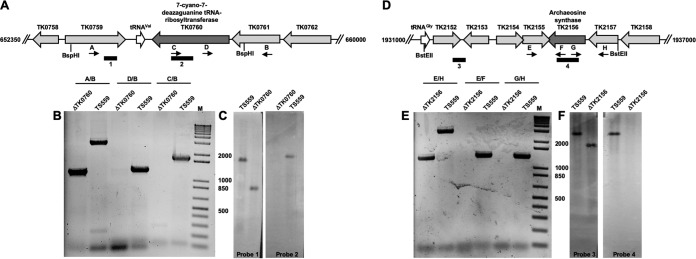
FIG 2.
T. kodakarensis strains with TK0760 (7-cyano-7-deazaguanine tRNA-ribosyltransferase) and TK2156 (archaeosine synthase) markerlessly deleted. (A and D) Map of the T. kodakarensis genome surrounding TK0760 (A) and TK2156 (D) in the parental strain TS559, highlighting the binding positions of oligonucleotides that were used in diagnostic PCRs (panels B and E, respectively) and Southern blots (panels C and F, respectively). (B and E) PCRs with primer sets listed above each lane generate amplicons from genomic DNA purified from strains TS559, ΔTK0760, and ΔTK2156. The external primer pairs (A/B for TK0760; E/H for TK2156) generate smaller amplicons from ΔTK0760 and ΔTK2156 genomic DNAs, respectively, reflecting the loss of TK0760- or TK2156-coding sequences. Amplicons generated using one primer complementary to the target locus and one primer complementary to flanking sequences are generated only from TS559 genomic DNA, consistent with deletion of the TK0760- or TK2156-coding sequence, respectively. (C and F) Southern blots of digested total genomic DNA from strains TS559, ΔTK0760, and ΔTK2156 demonstrate deletion of TK0760 or TK2156, respectively. Blots developed with an amplicon complementary to the TK0760-coding sequences (probe 2) reveal a complementary target only from TS559 DNA, while an amplicon probe complementary to adjacent sequences (probe 1) within the same BspH1 fragment reveals a smaller target, consistent with deletion of TK0760-coding sequences. Blots developed with an amplicon complementary to the TK2156-coding sequences (probe 4) reveal a complementary target only from TS559 DNA, while an amplicon probe complementary to adjacent sequences (probe 3) within the same BstEII fragment reveals a smaller target, consistent with deletion of TK2156-coding sequences. Numbers between panels B and C and between panels E and F are DNA fragment sizes in base pairs. Lanes M, DNA standards.