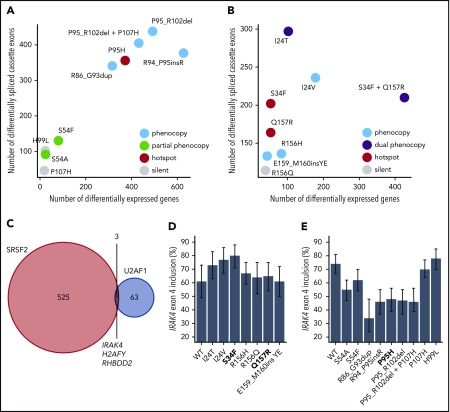
Figure 4.
Hotspot and rare SRSF2 and U2AF1 induce transcriptome dysregulation and converge on H2AFY and IRAK4 mis-splicing. (A) Scatter plot comparing the numbers of differentially expressed genes (x-axis) and differentially spliced cassette exons (y-axis) in K562 cells expressing each indicated SRSF2 mutation vs WT-expressing control cells. Differentially expressed genes were defined as those genes with expression at least 1 TPM in both samples, |log2 (fold-change)| ≥log2 (1.5), and Bayes factor at least 10. See Table 1 for additional information on classification of each mutation. (B) As panel A, but for the indicated U2AF1 mutations. (C) Venn diagram illustrating the sets of coding genes containing cassette exons and mutually exclusive exons that were differentially spliced in association with both hotspot and rare SRSF2 and/or U2AF1 mutations relative to control WT-expressing cells. Differentially spliced exons were defined as those exhibiting a change in isoform ratio at least 10% and a Bayes factor at least 1. Diagram restricted to genes containing cassette exons or mutually exclusive exons that were differentially spliced in association with at least 3 SRSF2P95-like mutations (SRSF2R86_G93dup, SRSF2R94_P95insR, SRSF2P95H, SRSF2P95_R102del, and SRSF2P95_R102del + P107H considered) and 3 U2AF1S34-like mutations (U2AF1I24T, U2AF1I24V, and U2AF1S34F considered). (D) Inclusion of a cassette exon within IRAK4 in K562 cells expressing each indicated U2AF1 allele. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals as estimated by MISO.55 (E) As in panel (D), but for cells expressing each indicated SRSF2 allele.