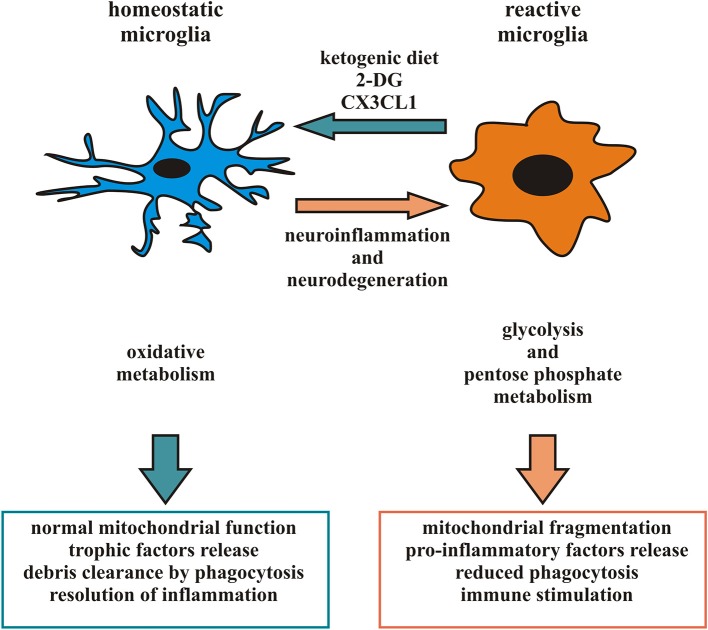
Figure 1.
Microglia phenotype and metabolic state: in response to appropriate signals, reactive microglia can switch from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory phenotype and vice versa, reorganizing their structure and functions. In particular, pro-inflammatory microglia release cytokines and free radicals that impair brain repair and regeneration while anti-inflammatory microglia resolve cerebral inflammation and promote brain repair increasing phagocytosis and release of trophic factors. Different phenotypes of microglia are associated to distinct metabolic pathways, in order to perform their different functions and their activation leads to changes in mitochondrial dynamics and switch among oxidative phosphorylation and glycolytic metabolism. Several neurodegenerative diseases have been associated with neuro-inflammation related to microglia hyperactivity or mitochondrial dysfunction. Factors able to promote an anti-inflammatory microglia, such as a ketogenic diet, 2-DG and CX3CL1, may represent an intriguing approach to counteract some aspect of neurodegenerative diseases.