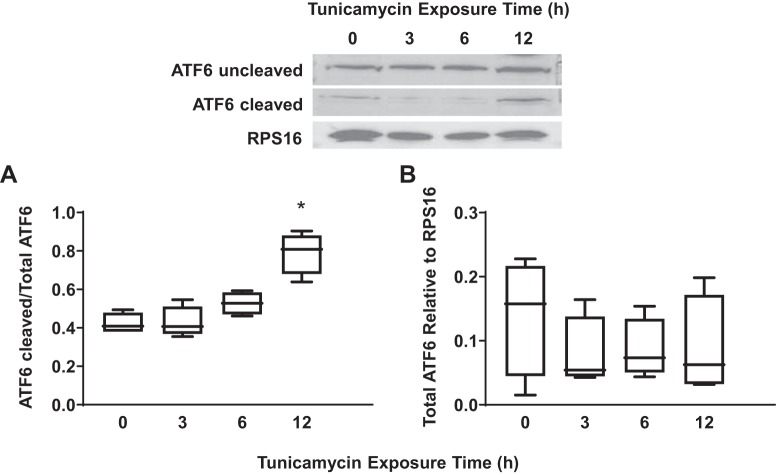
Fig. 3.
Exposure to tunicamycin activates the activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) pathway in airway smooth muscle (ASM) cells. A: 12-h exposure to tunicamycin significantly increased the ratio of cleaved to uncleaved ATF6 in ASM cells compared with untreated controls. Representative Western blots are shown. B: exposure to tunicamycin did not significantly change total ATF6 expression [relative to ribosomal protein S16 (RPS16)] in ASM cells compared with untreated controls. Data are presented as medians and interquartile range (IQR) represented as a box-and-whisker plot. Results were analyzed using a 2-way ANOVA. Untreated controls for each time point were performed. *Significant difference (P < 0.05) compared with untreated control (n = 5 patients).