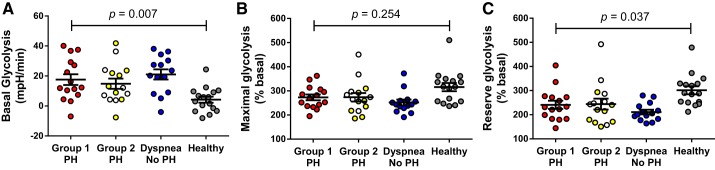
Fig. 2.
Platelet glycolytic metabolism in patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH), patients with dyspnea, and healthy controls. Basal glycolysis (A) was increased, whereas reserve glycolysis (B) was decreased in group 1 PH platelets (n = 15, 10 females) compared with healthy control platelets (n = 16; 12 female) but did not differ from platelets of group 2 PH (n = 15; 13 female) or dyspnea patients with no PH (n = 14, 12 female). C: reserve glycolysis is the difference between basal and maximal glycolysis, which also trended lower in group 1 PH vs. healthy control platelets. Group 2 PH includes patients with isolated post-capillary PH (○) and combined pre- and post-capillary PH (yellow circles). Graphs show means ± SE. P values were calculated using 1-way ANOVA, with post hoc Dunnett’s test between group 1 PH and healthy controls (basal glycolysis) and Kruskal-Wallis test with post-hoc Dunn’s test between group 1 PH and healthy control (maximal and reserve glycolysis).