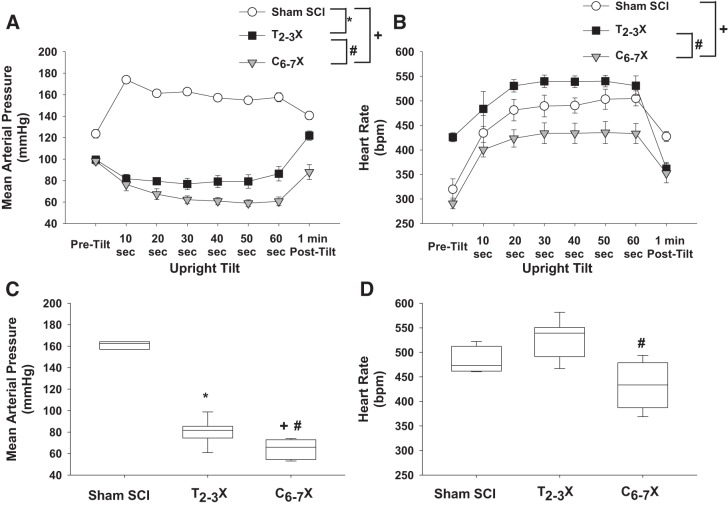
Fig. 9.
A and B: arterial pressure (A) and heart rate [beats/min (bpm); B] responses before upright tilt (Pre-tilt), during upright tilt, and at 1 min after upright tilt (Post-tilt) for t spinal intact (Sham SCI), paraplegic (T2–3X), and tetraplegic (C6–7X) rats. C and D: box and whiskers plots averaged over 1 min. In Sham SCI rats, upright tilt increased blood pressure. In contrast, upright tilt decreased blood pressure in paraplegic rats, and the decrease was significantly greater in tetraplegic rats. Although upright tilt increased heart rate in all groups, the response was significantly lower in tetraplegic rats compared with paraplegic and spinal intact rats. *P < 0.05, Sham SCI vs. T2–3X, group effect; #P < 0.05, T2–3X vs. C6–7X, group effect; +P < 0.05 Sham SCI vs. C6–7X, group effect.