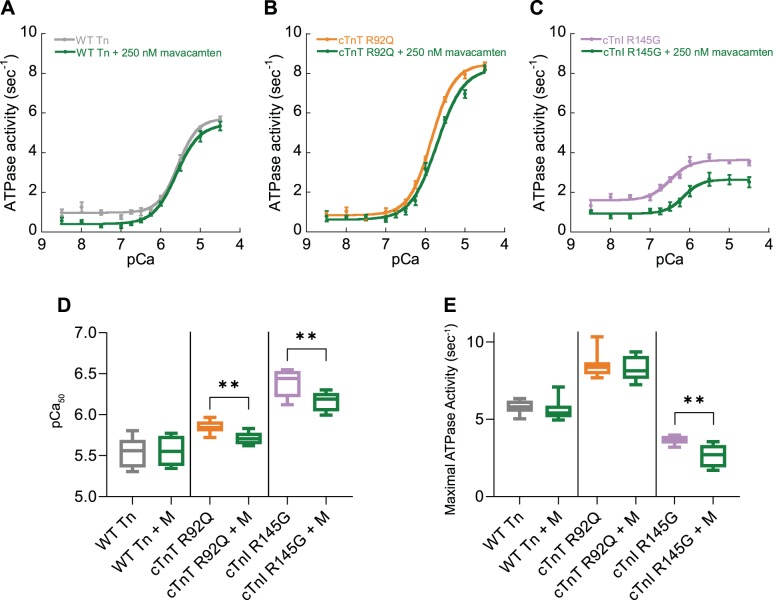
Fig. 1.
The effect of mavacamten on the myofilament ATPase. Myofilament function was assessed using in vitro actin activated actomyosin S1 ATPase assays. Myofilaments containing wild-type (WT) troponin (Tn) complexes (gray; A, D, and E), troponin complex reconstituted containing cTnT R92Q subunits (orange; B, D, and E), or cTnI R145G (purple; C, D, and E) were compared with those treated with mavacamten (M, green; A–E); n = 8, means ± SE. −Log [Ca2+] required for half maximum ATPase activity (pCa50; D) and maximal ATPase activity (E) are plotted comparing either wild-type troponin, troponin containing troponin T (TnT) R92Q, or cardiac troponin I (cTnI) R145G subunits with those treated with 250 nM mavacamten. Box and whisker plots (D and E) give the median average, interquartile range (box), and minimum and maximum data spread (whiskers). **P < 0.01, using Student’s t-test (D) or Mann-Whitney test (E) comparing mutant troponin to mavacamten-treated mutant troponin.