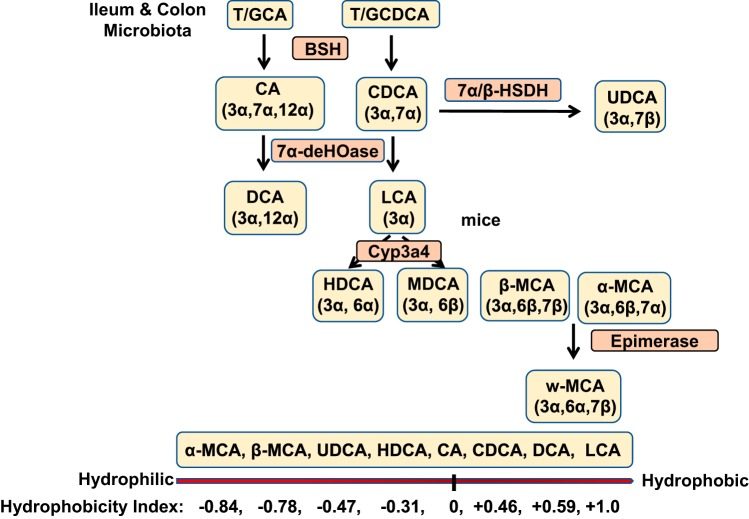
Fig. 2.
Bile acid transformation in the gut. The primary bile acids are transformed to secondary bile acids by gut bacteria. Bile salt hydroxylase (BSH) deconjugates glycine (G)/taurine (T)-conjugated bile acids, then bacterial 7α-dehydroxylase removes a 7α-HO group from chloric acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) to form deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA), respectively. CDCA is converted to ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) by 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7βHSDH). UDCA can be converted to LCA by 7β-dehydroxylase. In mouse liver, CDCA and UDCA are converted to α-muricholic acid (MCA) and β-MCA by Cyp2c70, and β-MCA is converted to ω-MCA by 6β-epimerase by the gut bacteria. CDCA also can be converted to hyocholic acid by 7α-epimerase in human and pig livers. In mice, LCA can be hydroxylated to hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA) and murideoxycholic acid (MDCA). DCA and LCA can by rehydroxylated to CA and CDCA, respectively, in mouse liver. Bile acid hydrophobicity index is shown at the bottom.